Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Do you wonder how do fishing nets work? This essential guide explores the core mechanics behind these tools. We will cover the principles of gilling and trapping. You will also learn about different net designs and the strands used to make them. Our goal is to help you choose the best fishing net for your needs.
What Defines a Fishing Net’s Function?

As experienced manufacturers, we want to explain the details of how fishing nets work for different applications. A fishnet represents much more than just a piece of thread; it functions as a highly precise tool. The fishing net type has two main parts: Selectivity and Method. Selectivity specifically determines what the type of fish net catches, while the Method defines how that fish catching net actually captures a fish. This detailed guide will explain the core mechanics of fishing nets, covering all the different types of fishing nets you might encounter.
We will examine everything from simple hand net fishing tools to complex commercial fishing nets like trawl nets. Having a clear understanding of these types of nets allows you to select the most appropriate fishing gear nets for your goals. We have found that fishing with nets is truly an intricate and fascinating science.
The Core Mechanics: How Do Fishing Nets Work?
Net fishing captures fish in many different ways. In this section, we will analyze the most important principles of capture.
A. The Gilling Principle

The gilling principle is simple but also highly effective. This specific technique is called gillnetting. You can think of gill nets as selective walls. These nets for fishing hang vertically within the water. We engineer the gill net mesh size for a very specific target fish. This engineering is the key to how does a gill net work. Fish swim directly into the fish netting.
They often do not see the thin fishing netting material. Their heads pass through, but their larger bodies do not. When they try to reverse, the twine catches their gill plate. This simple mechanism is what experts call selectivity. Understanding this helps solve some, but not all, gillnetting problems. Many people ask, ‘what is a gill net?’ The simplest answer is: a passive fence.
My first time seeing a gill net in action, I was amazed at its simplicity. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service notes that “gillnetting, when used properly, can be a valuable tool for monitoring fish populations.” But what makes it work so well?
1. Gill Plate Capture
50mm Mesh
A 50mm mesh is a very precise measurement. This size directly relates to how a gill net works for a specific species. This measurement is a ratio based on a fish’s specific body diameter.
Target Size
The mesh size absolutely must correspond with the target fish’s size. For example, a 100mm opening is designed for catching large fishing net targets. This critical detail ensures the net’s selectivity.
Forward Swim
Fish move with a forward swim. They often have no sight of the thin fishing netting in the water. This lack of visibility is exactly what makes gill netting successful.
2. Vertical Hanging
Float Line
A Float Line is a critical rope fishing net component. It is always at the top of the fishing net. This component helps to keep the top of the gillnet suspended on the water’s surface.
Lead Line
The lead line is the weighted rope at the bottom, and it sinks. It vertically pulls down the fisherman net, holding it open.
Water Column
The fishing using net hangs straight in the water column. This configuration effectively snags fish that swim between depths of five and 15 meters.
3. Selective Mesh
Juvenile Escape
A correct mesh size allows juvenile fish to escape. This is critical to sustain the future fish population. This way, only mature fish are taken.
Species-Specific
Gillnet fishing can be very species-specific. For example, a 7-inch mesh will not snag a 4-inch perch. This selectivity is essential for modern fishing.
NOAA Rules
Agencies like NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) often regulate mesh size. This is done to protect fish stocks. For example, a specific regulation might require 6-inch openings to protect certain species.
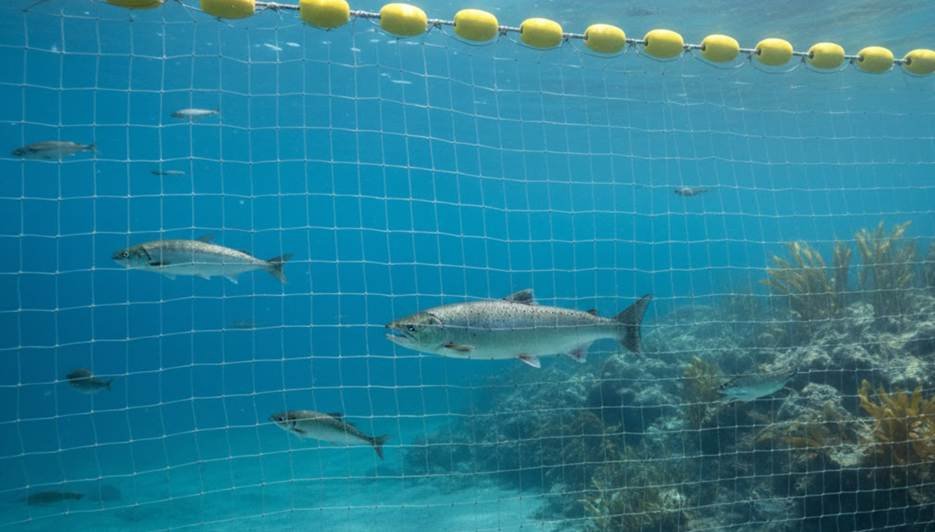
B. The Entanglement Method

The entanglement method is performed with a specialized tangle net. The trammel net is a perfect example of this. This is a very clever fishing net built with three distinct layers. It features three walls of fish netting hung on the same line. The two outer walls use a large, coarse mesh. In contrast, the inner wall is a very loose, fine mesh fishing net.
When a fish swims into this three layered fishing net, it easily passes the first large mesh. Then, it pushes the fine inner netting through the second large outer mesh. This action forms a pocket, and the fish gets hopelessly entangled. This specific design is how trammel nets work so well for bottom fish. This kind of fishing net is incredibly effective.
I’ve seen fishermen pull up trammel nets with a fantastic catch of flounder. As Oceana points out, “Trammel nets… are used to catch fish (such as flatfish, sole, and flounder) and crustaceans that live on or near the seabed.”
1. Trammel Net Design
Three Layers
This fishing net design features three distinct layers. It has two outer walls and one inner wall. This 3 layer fishing net system is remarkably effective.
Fine Inner Mesh
The fine inner mesh is hung very loosely. It typically has a small 25mm mesh fish net. This is the specific part that actually tangles the fish.
Large Outer Mesh
The large outer mesh walls are stiffer. These walls may have large 150mm openings. They are essential for creating the bagging action.
2. Bagging Action
Fish Pushes
The fish pushes the fine inner net for fish. This push is the start of the bagging action. In essence, the fish does all the work.
Inner Bag
The fish itself creates an inner bag. This bag is formed from the loose, fine mesh. The fish pushes this fine mesh through the large mesh gill nets on the other side.
Tangle Capture
This tangle capture is very secure. The fish becomes wrapped tightly in the pocket. There is no easy escape from this fishing net trap.
3. Bottom Dwellers
Flounder Nets
Trammel netting is ideal for creating flounder nets to catch fish. These fish live directly on the seafloor. They are generally not fast swimmers.
Seabed Contact
The weighted fishing net must have good seabed contact. The lead line must rest firmly on the bottom. This contact stops fish from swimming under the net.
Low Mobility
This net fishing technique works very well for low-mobility species. Crabs and flounder are common catches with this type of net.
C. The Encirclement Strategy
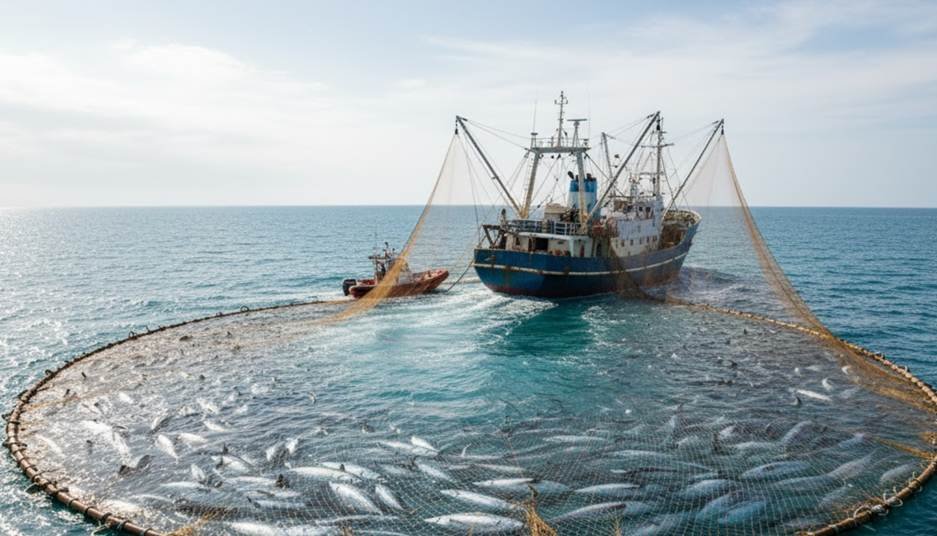

A good example of the encirclement strategy involves commercial fishing nets. The purse seine action is a key example. Unlike a passive drift net, a purse seine is an active net fishing method. A boat actively circles a school of fish. One of the most common types of net fishing gear is the purse seine. After circling, the fishing net is pulled shut from the bottom.
This process is often called ring netting. It works just like a drawstring on an old purse. This method is even how do salmon fishing nets work in some large fisheries. It captures almost the entire school in the giant fishing net, which is why it’s used for fishing with nets in the ocean. A similar, shore-based method is called haul seine fishing.
Have you ever seen footage of a purse seiner in action? It’s an incredible display of coordination. The first time I saw one, the sheer scale of the operation was hard to believe, closing a huge fishing net around an entire school of tuna.
1. Purse Seine Action
1000m Length
These large fishing nets are truly huge. One of the biggest fishing net types, a purse seine can be almost 1000 meters long. It can also go 200 meters deep into the water.
Drawstring Bottom
The drawstring bottom is the key feature. A “purse line,” often a strong steel cable, can be 1200 meters long. This purse line closes the fishing net bottom.
Closing Rings
Closing Rings, which are large steel rings, are lined up along the bottom of the net and fish are trapped inside. This heavy steel line pulls through the rings to close the fish catching net.
2. Surface Targeting
Pelagic Species
This method is a unique fishing net strategy because it targets fish in nets that school near the surface. Common targets include tuna and mackerel.
Tuna Schools
Captains first spot the tuna schools from the fishing boat net-equipped vessel. The fishing net is then deployed. The boat circles the entire school very quickly.
Mackerel Hauls
This fishing using net method is also used for mackerel hauls. A single haul can capture over 50 tons of fish. It is an extremely efficient fishing technique.
3. Boat Operation
Skiff Deployment
A small boat, known as a skiff, holds one end of the fishing net. This skiff deployment anchors the net for fishing. The main boat then circles the fish.
Net Circling
The main vessel performs the net circling operation. This action must be very fast. It must be completed before the fish in a net can escape.
Power Block
A hydraulic power block is used for retrieval. This powerful winch hauls the giant fishing net back. It lifts the heavy catching net aboard the vessel.
D. The Funneling Mechanism
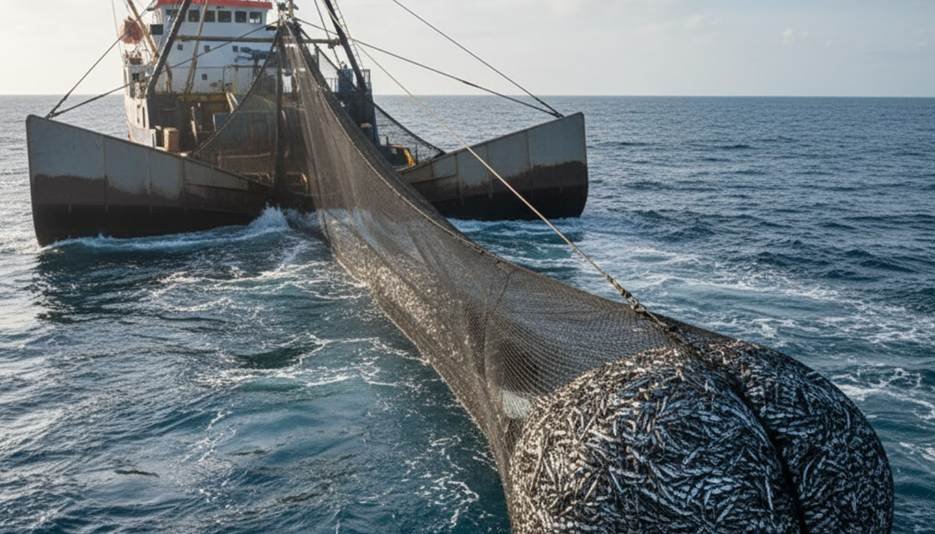

The funneling mechanism is used by trawl nets. These nets are also commonly called drag nets. This is an active fishing method. A boat pulls a large conical net through the water. This big fish net effectively funnels fish. The fish are pushed to the very back of the net. These ocean fishing nets are very large. In fact, they are some of the largest fishing nets used in the world. They can be over 60 meters long. This dragnet fishing net is a common type of ocean netting in marine nets fisheries.
Trawling is a powerful, but controversial, method. The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) states, “Trawling… can have a significant impact on the seabed… MSC certified fisheries are required to minimize their impacts.” This is why net design is so critical.
1. Trawl Net Shape
Cone Design
The intentional cone design flows smoothly from a wide mouth to a narrow end. This shape is designed to funnel all fish caught net.
Wide Mouth
The mouth of the net can be tremendously wide. For a pelagic trawl, it can be 100 meters wide. This width helps cover a large net area.
Cod-End Bag
The end of the trawl is a fishing bag net where fish school up. This part is termed the cod-end bag. It typically has a smaller cod-end fishing mesh of 120mm.
2. Active Towing
3 Knots Speed
The boat tows the net at a very slow speed of 3 knots. This slow speed is the optimal fish-herding speed.
Otter Boards
These are heavy, hydrodynamic steel doors. They are crucial for keeping the fish net mouth open horizontally.
Warp Lines
These are the thick steel cables that connect the otter boards to the vessel. They tow the entire fish net trap through the water.
3. Herd and Capture
Fish Funneled
All the fish in net are herded. They are funneled toward the cod-end by the net’s wings.
No Escape
Once the fish are in the cod-end, there is absolutely no escape. This is due to the water pressure and the 12-ton load of fish.
12-Ton Loads
The cod-end has to be extremely strong. It must withstand 12-ton loads of fish. This requires very high-strength fishing netting.
E. The Passive Drifting Technique
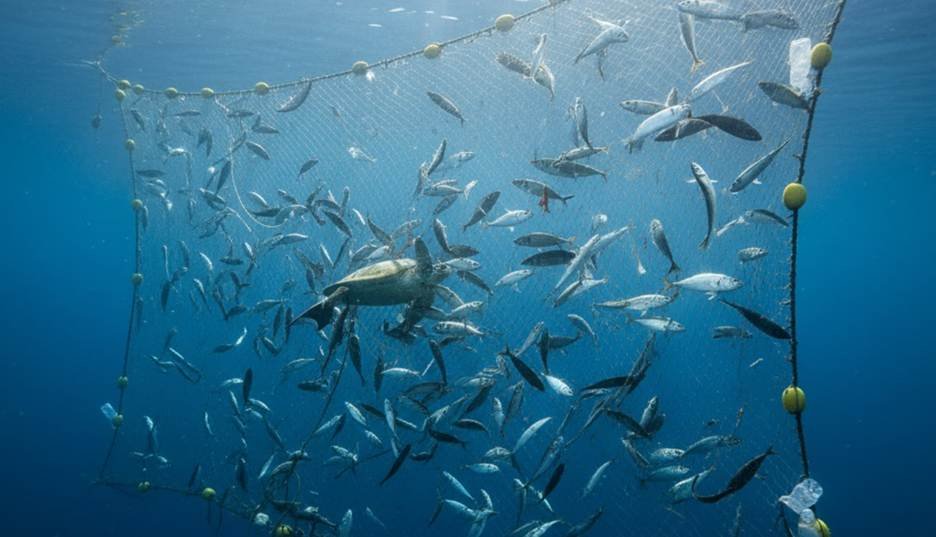

The passive drifting technique is quite simple. This method uses current propulsion to move. There is absolutely no towing involved. The fishing net ocean gear, or ocean net fishing gear, just floats. It forms a vertical wall of fishing netting. This wall drifts in the open water.
The main problem with this method is ghost fishing. So, what is ghost fishing? It occurs when lost gear becomes a ghost net. This fishing waste continues to catch fish with net technology unmanned. This unmanned capture causes extremely high bycatch. Plastic fishing nets are a major source of this fishing pollution. This is a major environmental issue.
I’ve pulled up old, tangled ghost nets before, and it’s a sobering sight. The amount of marine life trapped is heartbreaking. Have you ever wondered what happens to lost fishing gear net items?
1. Current Propulsion
No Towing
This method involves no towing at all. The net moves freely. It is pushed simply by wind and ocean currents.
Open Water
Drift nets are used in open water. They are not anchored to the seabed. They can cover many miles in a single set.
Migratory Species
They often target fishing net species. This includes salmon and squid. These fish travel long distances in the open ocean.
2. Ghost Fishing
Lost Gear
Lost fishing gear nets are the primary cause. Nets can break away during storms. This is a common issue with ghost fishing gear.
Unmanned Capture
The ghost nets continue fishing on their own. This unmanned capture kills marine life indiscriminately. This includes dolphins, turtles, and animals in nets.
High Bycatch
Ghost nets have extremely high bycatch rates. They catch fish net style anything that swims. They do not discriminate between species.
3. Net Deployment
Surface Buoys
Surface buoys support the fishing net with floats. The attached float line gives surface support to the net.
Vertical Wall
The net forms a vertical wall. This long fishing net can descend 15 meters in the water. Some drift nets have been 50 kilometers long.
Low Effort
This is a low-effort method. The crew only has to deploy the net. They can then pick it up many hours later.
F. The Trapping Principle
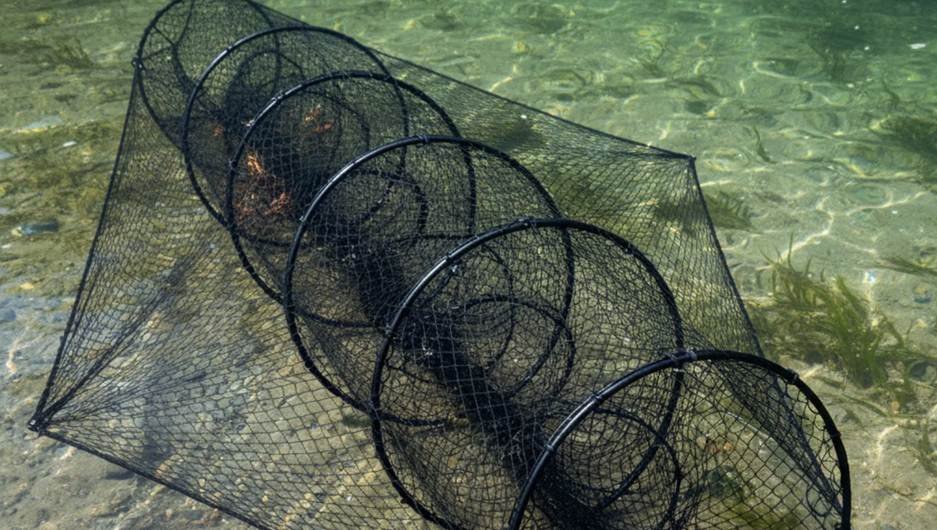

The trapping principle focuses on fish behavior. It uses design to navigate fish into the fishing net. The fyke net is a classic example of a passive capturing net. It is a bag net fishing method that uses “wings” to guide fish. The wings lead them to an entrance. Once fish swim through that entrance, they get trapped inside. These nets to catch fish are often baited. They are very effective for capturing species like eels and crayfish. We offer durable fyke nets for sale.
Traps like fyke nets are ancient designs. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) describes them as “traps…consisting of cylindrical or conical netting bags mounted on rings or other rigid structures…particularly effective for catching eels.”
1. Fyke Net Design
Hoop Structure
The structure that carries the netting and keeps it open is the hoop structure. These hoops can be 1 meter wide. They create a long, tunnel-like fish trap net.
Funnel Entrances
There are several non-return funnel entrances inside. These get progressively smaller. Fish that swim in cannot find their way back out.
Leader Wings
The long net walls set at an angle are called leader wings. They effectively funnel fish toward the first funnel entrance.
2. Passive Capture
Stationary Gear
This is a clear example of stationary gear. It is positioned on the river bed or seabed. It does not move.
River Beds
Fyke nets are often set on river beds. They are also utilized in lakes. They work best in still or slow-moving water.
Eel Traps
They are very effective as eel traps. This is because eels swim along the bottom. They hit the leader wings and are guided into the final bag.
3. Fish Behavior
Guided Movement
The net uses guided movement. Fish are steered by the leader wings. They tend to follow walls and do not try to swim through.
Non-Return
The non-return funnels ensure fish are lost. The fish becomes bewildered. It cannot figure out the small exit hole to escape.
Low Impact
This is a low-impact fishing method. The bycatch that does occur can often be released alive. This is because the net is not tightly woven and does not harm them.
G. The Scooping Method
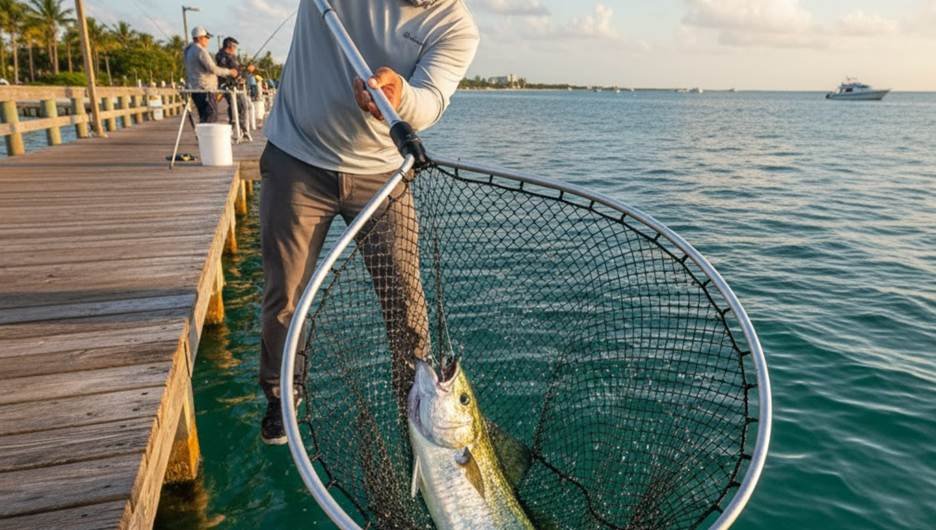

The scooping method uses hand nets. These fishing nets are attached to fishing net stick poles. These hand net fishing tools are typically small. This is a small-scale fishing tool. This kind of netting fish is very common. This is how fishing nets work for manually catching fish.
It works very well for catching bait or landing a hooked fish. This pole fishing net is a very simple tool. Many anglers use a hand net at piers. These small fishing nets are simple in design. They often consist of a metal fishing net frame.
We’ve all used a pole net fishing style, even if just as kids. I still keep a small fish net in my car for emergencies. Do you remember the first fish you ever caught in a hand net?
1. Handheld Operation
Long Handle
A long handle provides the fishing net on pole the user holds. This pole could be 8 feet long. It helps net fish from a boat or pier.
Manual Scoop
The fishing pole user has to manually scoop the fish. This is the simple action of scooping fish with a net. Timing is essential for this. You must ensure you get the fish’s head in the net first.
Small Scale
This method is meant for small-scale purposes only. This is not a commercial fishing technique.
2. Frame and Bag
Rigid Frame
A rigid frame is required to keep the bag open. This frame is usually made of aluminum. It could be 20 inches wide.
Mesh Bag
The mesh bag is the part that holds the fish. A net made of rubber mesh is ideal. It helps protect the fish’s sensitive slime coat.
Dip Nets
These are also known as dip nets. They are often used for scooping minnows from bait tanks.
3. Specific Uses
Bait Retrieval
One of the main purposes is bait retrieval. You can catch bait live with your net in a livewell. This is often a common 10-inch net.
Landing Fish
The main purpose for anglers is landing fish. A standard-sized large fish net can accommodate a 20-pound fish.
Aquarium Use
The use of fishing nets in aquariums is also common. A fine mesh fishing net is used for transporting delicate fish.
H.The Filtering Process
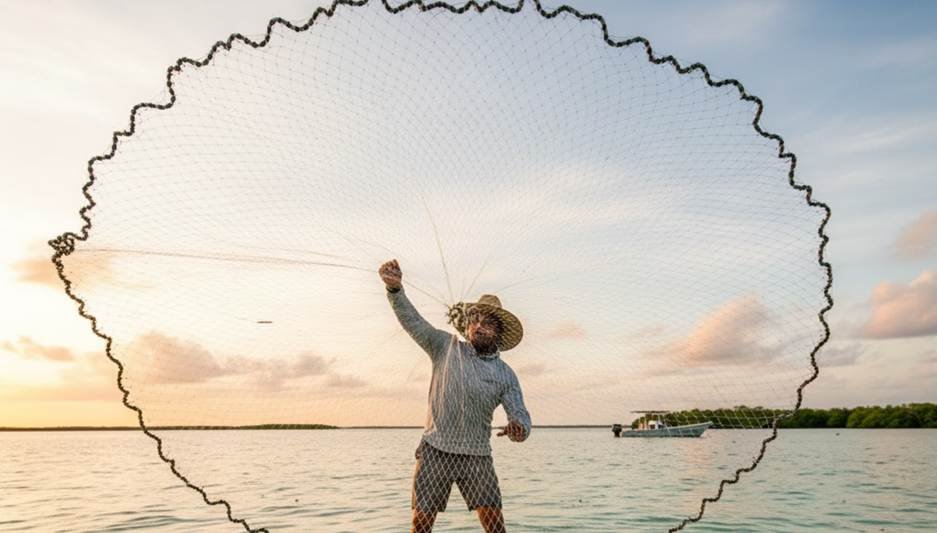

The filtering process is what a cast net is all about. A cast net is a circular net used for fishnet fishing. This is what a common throw net is. The cast net technique is a simplified form of net fishing. One of the main net fishing techniques is throwing this net. A person throws the casting net by hand.
How do throwing fishing nets work? When someone throws the net, it opens automatically in the air. After which, the net lands on the water. This is also known as throwing fish nets. The weighted fishing nets then descend. It catches fish as it sinks. Cast nets are used very often to catch baitfish. This is called cast net fishing. Learning how to throw a fishing net requires practice.
Casting a net perfectly is a real skill. I’ve seen experts throw a castnet so it opens in a perfect circle every time. “A properly thrown cast net should open fully, forming a ‘pancake’ on the water’s surface,” according to a guide from Salt Water Sportsman. Have you ever tried to master the cast net throw?
1. Cast Net Technique
Hand Thrown
The cast net is hand thrown. This is the hand thrown technique for throwing fishing nets. This is the central and most important technique for cast net throwing.
10ft Radius
A castnet can open to a 10-foot radius or even wider. Some 10-foot cast nets for fishing can span over 300 square feet.
Circular Spread
A perfect circular spread represents a successful net throw. This casting a net method is how you trap the greatest amount of fish.
2. Sinking Action
Lead Weights
Lead weights are sewn into the lead line. They typically range from 1.5 pounds per foot of net.
Fast Sink
Weighted nets with over 1.5 pounds of lead per foot sink very rapidly. This how do cast nets work fast sink rate assures fish have no chance to escape before the net hits the bottom.
Shallow Water
These fishing nets perform best in shallow water, usually less than 15 feet deep.
3. Retrieval Capture
Bottom Closure
A pull rope, or hand line, is a key fish net component. When you pull it, it closes the bottom of the net, trapping the fish inside. This explains how does a cast net close.
Baitfish Capture
This is perhaps the easiest way to catch fish with a cast net. Shrimp and mullet are easily available and simple to catch with this method.
HMPE Vs. Nylon: A Material Comparison!

Selecting the fishing net material is a very substantial decision. In this section, we will compare HMPE and conventional Nylon (PA6).
HMPE (UHMWPE)
HMPE (UHMWPE), or ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, is one of the best fishing nets material options. This is because of its incredible strength-to-weight ratio. Other fibers can make adequate fishing net materials, but they will not be as thin, light, and drag-resistant as nets made from this advanced fish netting material.
Nylon (PA6)
Nylon (PA6) is another primary nylon net for fishing material. Nylon fish netting comes with the benefit of easily stretching. Nevertheless, a nylon fishing net becomes rather cumbersome once it is soaked with water. Fishing nylon net products tend to gain significant water weight. As a supplier, I’ve handled both. A wet nylon fishing net is incredibly heavy. A same-sized HMPE net feels almost dry by comparison. This difference is a game-changer for crews who pull nets all day.
HMPE: 15x Steel
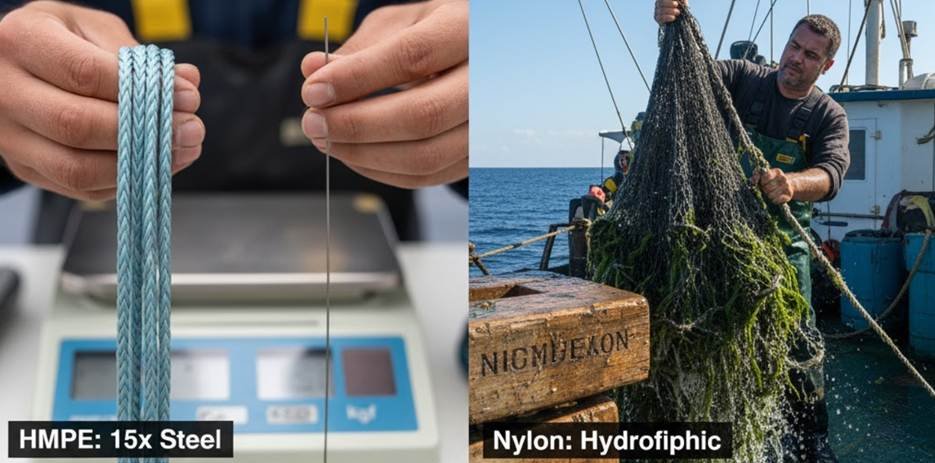
You have probably heard that HMPE is 15 times stronger than steel of the same weight. This implies that a 10mm HMPE twine can substitute for a much thicker steel cable. This strength is important for trawl warps and all other components of the fishing mechanism.
Nylon: Hydrophilic
Nylon fishing nets absorb water. In fact, they can gain 10% of their weight in water. This moisture absorption is a key trait. Nylon fishing nets have a heavy configuration when wet. This means drag is heavier, and therefore, more fuel is required to tow them.
HMPE: Floats (0.97)
A net made with HMPE material floats. This is because the specific gravity of HMPE is 0.97, which is less than water (1.0). This floating property is key to why nets made from this material have extremely low drag and are easier to pull.
Nylon: Sinks (1.14)
Nylon Sinks. Its specific gravity is 1.14. This in turn makes the net’s weight rather heavy in the water. It takes an immense amount of pressure to tow. Consequently, this heavy drag makes your fuel expenses skyrocket over time.
HMPE: High UV
HMPE has high UV resistance. Moreover, it does not degrade in direct sunlight. This is the reason why our nets can last 5 years or more. This durability is a key feature of our products.
Nylon: Degrades
Nylon degrades in the sun. The sun’s UV rays disintegrate the polyamide 6 fibers. Within a net, the result is extreme brittleness. After only one season, the net can lose significant strength. This results in an immense long-term cost.
Understanding Key Fishing Net Specifications!

Understanding key fishing net specifications is vital. Specs can be confusing, but they define how fishing nets work. As the Gulf Coast Research Laboratory explains, “Mesh size is the most important factor in determining the size of fish a net will catch.” Let’s look at the specs that matter.
Mesh Size (mm)
Mesh Size (mm) is perhaps the most critical specification for selectivity. This measurement, taken from knot to knot, determines what size fish the net will catch or retain. A small fish nets mesh might be 10mm for bait, while a gill net for salmon might be 150mm.
Twine Diameter
Twine Diameter refers to the thickness of the fishing netting material itself. A thicker twine, like 2mm, offers higher breaking strength and abrasion resistance. A thinner twine is less visible to fish but may break more easily.
Breaking Strength (Kgf)
Breaking Strength (Kgf) measures how much force, in kilograms-force, the net twine can withstand before breaking. For heavy duty fishing net applications like trawling, a very high breaking strength is absolutely essential.
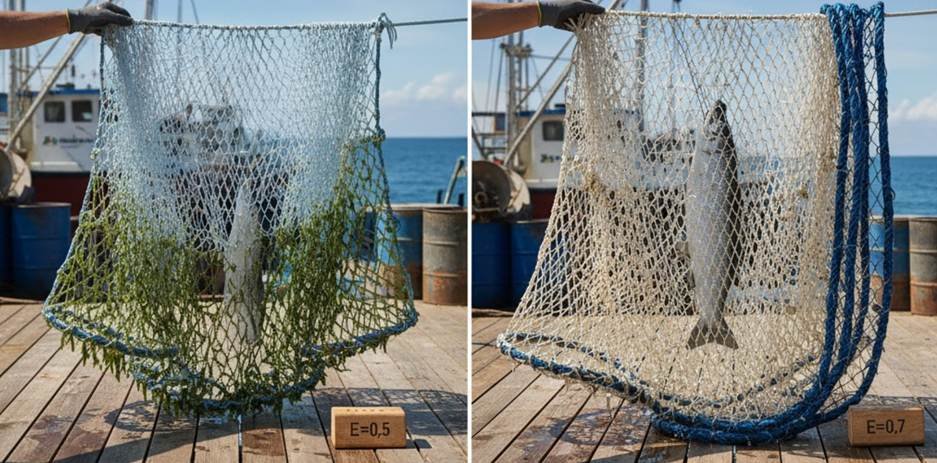
Hanging Ratio (E)
The Hanging Ratio (E) is a technical specification that defines the shape of the mesh. It is the ratio of the length of the rope to the length of the netting it is hung on. A low ratio (e.g., 0.5) creates deep, diamond-shaped meshes perfect for gilling. A high ratio (e.g., 0.7) creates open, square-shaped meshes ideal for trawls.
Knot Type
The Knot Type is also important for durability. Single knots are common and efficient but can slip in some nylon materials. Double knots are bulkier and create more drag, but they provide superior knot strength and stability, which is crucial for a fishing net fishing in rough conditions.
Antifouling Coatings
Antifouling Coatings are crucial for nets left in the water, such as aquaculture cages. We often use a special PU coating. This coating prevents marine growth like algae and barnacles. It extends the life of the fishing nets significantly. It also maintains the fishing nets’ buoyancy and effectiveness by keeping them clean and light.
UV Stabilization
UV Stabilization is required for any net used outdoors. The sun breaks down polymers, weakening the net. We add stabilizers to our HMPE fibers. This protects the net from sun damage. It helps guarantee a 5-year lifespan, which is part of the fishnet definition of quality.
| Specification | Primary Function | Unit/Type | Example Value(s) | Impact on “How it Works” | Common Net Type |
| Mesh Size | Selectivity | mm | 10mm – 150mm | Gilling; Juvenile escape | Gill Net, Trawl |
| Twine Diameter | Strength/Visibility | mm | 0.5mm – 2.0mm | Abrasion resist; Low visibility | All Nets |
| Breaking Strength | Load Capacity | Kgf | >500 Kgf | Withstands heavy loads | Trawl Net |
| Hanging Ratio | Mesh Shape | E (Ratio) | E=0.5 / E=0.7 | Diamond (Gilling) / Square (Trawl) | Gill Net, Trawl |
| Knot Type | Durability | Type | Single / Double | Knot stability; Drag | Knotted Nets |
| Coatings/Treatments | Longevity | PU / Additive | N/A | Anti-fouling; UV protection | Aquaculture, All |
Core Fishing Net Specifications: Mechanics and Impact!
How Do Fishing Nets Work in Aquaculture?
In aquaculture, nets are used for confinement. They create a safe enclosure that offers shelter to the fish. I’ve visited salmon farms, and the scale of the fish cages is astounding. They are like floating cities. But have you ever wondered how they protect the fish inside?
Fish Cages
Floating farms are referred to as fish cages. These net for fish structures hold thousands of fish. They are often 50×50 meters. These fish farm nets are tethered in bays or the open ocean.
Predator Protection
A main task of the net is predator protection. The net has to be extremely sturdy. It must stop seals and sharks. A heavy duty fishing net is needed. A hungry seal can easily damage 3mm nylon.
UHMWPE Cages
Our UHMWPE fishing cages are the best solution. They are 15 times stronger than steel. They easily stop predators. This is very important for netting for fish on aquaculture farms.
Knotless Design
We use a knotless design, and this is important for all fish caught in the net. Knots can hurt fish, causing injury and undue stress. A net without knots leads to better long-term fish health.
High Water Flow
Knotless nets also improve high water flow. This is important for the fish’s oxygen supply. Good water flow delivers oxygen and removes waste, which is vital for fish in a net at high density.
Antifouling PU
We apply an antifouling PU coating. This ensures the fish nets do not get clogged. Algae growth is a major problem. Fouling nets block water flow. Our coating reduces net maintenance by 60%.
Reduced Escapes
Strong caging means decreased escapes. A single 6-meter hole has the potential to lose 50,000 salmon. Our strong nets stop that from happening. This can save you 2 million dollars.
5-Year Lifespan
Your net comes with a 5-year lifespan. Other nets may only last 2 years. Investing in long-term savings with durable nets is a smart investment.
Regulation Compliance
We pass all regulation compliance. This covers nets standards conditions like NS 9415. Legal requirements for fish breeder nets are important. It makes sure the product passes quality verification.
Why Choose Duracordix HMPE Over Traditional Nets?

It is an obvious answer. Our nets made with HMPE provide real, measurable benefits.
Superior Strength
All our nets have superior strength. We are one of the premium fish net suppliers. We use HMPE. This material is 15 times stronger than steel. This equates to minimal tears and a much longer lifespan.
Lightweight (70%)
All our nets have a lightweight (70%) feature. Our nets are 70% lighter than a wet nylon net. This allows for effortless handling. This provides a significant advantage for your team.
Zero Water Retention
HMPE has zero water retention. It does not absorb water. It retains the same weight, whether it is wet or dry. This is a major difference from nylon.
Fuel Savings
The net drag reduction aids in fuel savings. Trawlers report savings between 20-35% while using our net. This is an excellent operational advantage.
Durable Twine
We found that many nets lose abrasion resistance. We use durable twine. This type of netting material is very useful. It can withstand abrasion from sand or contact with the seabed.
Reduced Workload
Reduced workload is one more advantage of using this net. The net’s weight reduction helps in hauling the net faster. The crew also ends the day less exhausted. This promotes better safety and morale on the working deck.
Cost Efficiency
The nets are also fairly cost efficient as they last 3-5 years. This is compared to a nylon net that lasts only 1-2 years. The long-term costs are dramatically lower.
High Abrasion Resistance
High abrasion resistance is critical. Our HMPE twines withstand cuts and rubbing against rocks during bottom trawling.
Knotless Vs. Knotted Netting Designs!
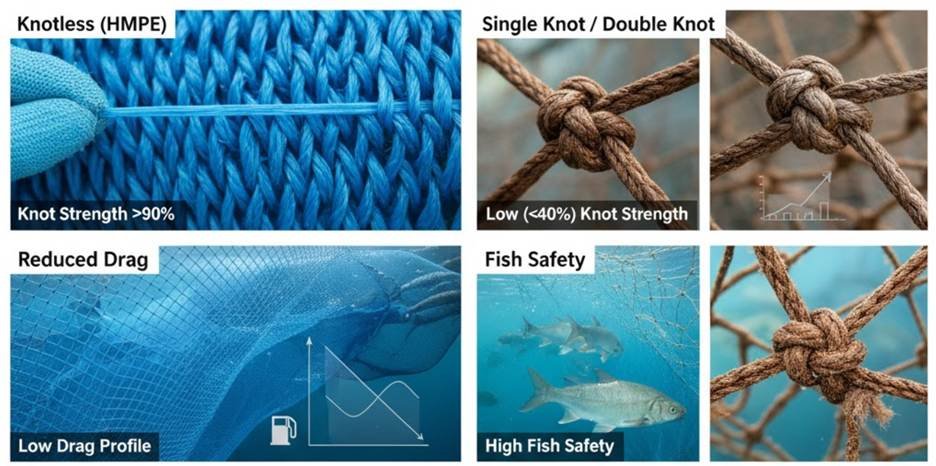

The way a net is constructed is just as important as the material. Let’s analyze the differences between knotless and knotted nets. I always check the knots on a new net. A poor knot is a failure point waiting to happen. But what if you could remove the knot entirely?
Knotless (HMPE)
Knotless netting is the modern solution. This fishing netting material is woven together. There are no knots. This is how to make a net for fishing that is incredibly strong.
Single Knot
A single knot is very common. This is often how to tie a gill net. It is a simplistic and efficient knot. However, this knot can be a significant weak point.
Double Knot
A double knot is much stronger. This knot is used in heavy fishing netting. It is bulky and creates more drag, but it is less likely to slip.
Knot Strength (90%)
Knotless joins are exceptionally strong. They retain over 90% of the twine’s original strength. A double knot can lose as much as 60% of the strength.
Reduced Drag
A knotless net has a smooth surface. This reduces drag in the water. The fuel savings are significant. This is a key benefit of this fishing net design.
Fish Safety
Aquaculture raises the question of fish safety. The knotless net surface is smooth. Over time, fish will be uninjured. This is a major contrast to nets with abrasive knots.
Higher Durability
Knotless nets generally have a higher durability factor. There are no knots to tighten or break. Knots are the place where fishing nets invariably fail.
Smooth Surface
The smooth surface nets are easier to clean. They do not allow algae or mussels to attach as easily. This is why they are perfect for fish cages.
| Feature | Knotless (HMPE) | Single Knot | Double Knot |
| Knot Strength | >90% (twine) | Low (weak point) | ~40% (twine) |
| Drag Profile | Low (smooth) | Moderate | High (bulky) |
| Fish Safety | High (uninjured) | Low (abrasive) | Low (abrasive) |
| Durability | High (no fail points) | Low (knot failure) | Moderate (slip resistant) |
| Maintenance | Low (resists biofouling) | High | High |
| Primary Use | Aquaculture / Cages | Gill nets | Heavy netting |
Netting Design: Technical Specification Comparison!
How Do Fishing Nets Work in Deep Sea Trawling?
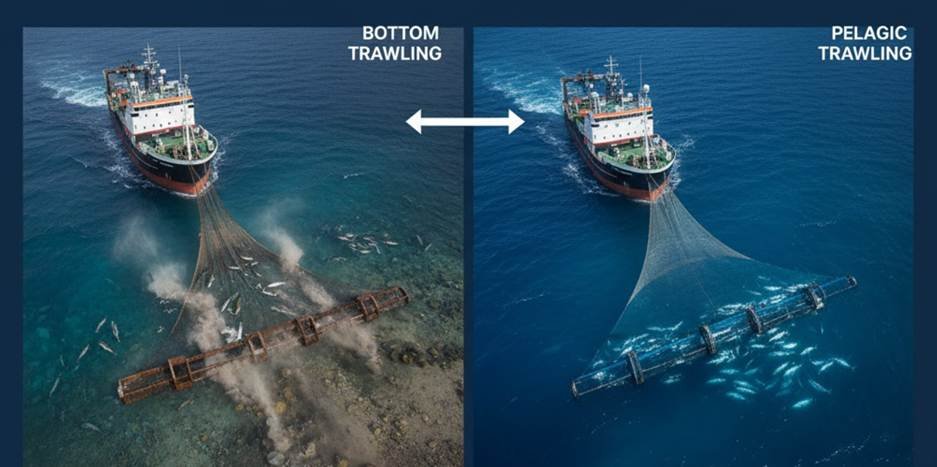

Deep-sea trawling is no walk in the park. The nets used must be exceptionally strong.
Bottom Trawling
Bottom trawling involves pulling a net that contacts the seabed. This ocean fishing net is used to catch cod and flounder. It is a very heavy-duty piece of work.
Pelagic Trawling
Pelagic trawling is when the net is “fished” in mid-water. There is no contact with the seabed. The target is mackerel, which makes this fishing easier with less work.
4-Panel Nets
Many modern trawls consist of 4-panel nets. This design is common in fishing gear because it creates a stable, square opening. It is much more favorable than older 2-panel nets.
Otter Boards
Otter boards act as the wings of the trawl. These 3-ton steel doors are a vital part of commercial fishing nets. They help spread the net mouth wide open.
Cone Funnel
The body configuration has a cone funnel shape. The net is designed to catch fish and funnel them. It helps to confine fish toward the back. This developed design extends over 100 meters in length.
Cod-End Capture
The last pocket on the net is the cod-end capture bag. It is designed to hold all the fish. It is also the strongest part of the net.
Heavy Loads (12-Ton)
The net must be able to handle twelve tons. Our nets are made from HMPE materials. Other nets made from nylon would rip under this load.
HMPE Trawl Warps
The trawl warps on the net are also made from HMPE. These warps are lighter than steel. This improves the nets by making it easier to shoot the gear. This also saves on fuel.
Future Trends in Fishing Net Technology!
Fishing technology gets better every day. The most interesting trend is Smart Nets. These nets will have sensors integrated directly into them. Smart nets will provide real-time data. This is a far cry from the antique fishing nets used in the past. The future is intelligent fishing. A report from Wired on smart nets mentioned, “Sensors can tell fishermen the species, size, and quantity of fish entering the net, helping them avoid bycatch.” This technology is changing everything.
Sensor Integration
The most important part of this net technology is sensor integration. Nets will have cameras and sonar sensors. This will provide fish density data in the net to reduce bycatch.
Biodegradable Nets
Biodegradable nets are designed to prevent ghost fishing. These nets will dissolve completely if they are lost. This prevents lost nets from trapping marine life.
Recycled Polymers
We are also in the recycled polymers stage. This reduces fishing waste. We can use old fish nets to make new nets. This is much better than selling used fishing nets for sale.
Improved Selectivity
Improved selectivity is the desired outcome. Escape panels in future nets will let non-target species exit. This is a big change from an old fishing net.
GPS Buoys
GPS buoys will become standard. All fishing gear will be tracked by these buoys. If a net breaks off, used fishing net retrieval is easier. It helps crews find the lost nets.
Automated Retrieval
We will see automated retrieval systems. These may use drone technology for net retrieval. Removing these nets helps clean the ocean.
FAQs!
You have questions, and as experts in the field, we are ready to answer.
What Forces Keep Trawl Nets Open?
There are two main forces in use. The first is the hydrodynamic Otter Boards (trawl doors), which spread the net mouth open horizontally. The second is a float line that holds the top up.
How do gillnets work to catch only gills?
Gillnets use precise mesh sizes that correlate with the desired catch. They capture target species with a net their head can fit through, but not their body. When caught in a fish net, their attempts to escape result in gill entrapment.
What Is a Net’s Hanging Ratio (E)?
The hanging ratio (E) is a crucial figure. It represents the dimension and shape of the fishing mesh. It is the ratio of the rope length to the stretched netting length. A 0.5 ratio results in deep diamonds. A 0.7 ratio results in wide squares.
How Do TEDs Eject Large Bycatch?
TED stands for Turtle Excluder Device. It is a grid contained within a trawl net. Smaller target fish nets species pass through the grid. Large bycatch, like turtles caught in nets, hit the grid and are steered to an escape hatch. This is a primary solution for target fishing net problems.
Why Does HMPE Fiber Float?
This is basic physics. HMPE has a specific gravity of 0.97. Water has a specific gravity of 1.0. Since HMPE is less dense than water, it floats. Nylon has a specific gravity of 1.14, which is why it sinks.
Conclusion
You now know about the types of nets and how do fishing nets work, from gilling to trapping. You also understand how advanced fibers like HMPE make nets lighter and more durable. These choices directly affect your catch. For the most durable and efficient fishing nets, visit Duracordix today.
About The Author

Moses Xu
Hi, I’m Moses Xu, VP and Marketing Director at Duracordix. With 10+ years in high-performance synthetic ropes and netting, I specialize in export trade and marketing. Whether it’s HMPE, Kevlar, or nylon ropes, I’m happy to share insights and connect!