Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Mooring Line?
A mooring line, also known as mooring rope or dock line, is a crucial piece of equipment used to secure marine vessels such as yachts, large ships, or oil platforms to docks, buoys, or anchorage points. It ensures stability during harsh weather, prevents dangerous movement, and is essential for safety, making it a vital part of marine equipment.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of mooring lines, their pros and cons for various applications, how to choose the right mooring rope, and address common issues, giving you a comprehensive understanding of mooring ropes.
Types of Mooring Line by Material

UHMWPE mooring line
UHMWPE mooring rope, also commonly known as Dyneema rope, is a woven rope made from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers. Renowned for its exceptional strength, lightweight design, and outstanding corrosion resistance, it is an ideal choice for enhancing mooring stability and safety in harsh marine environments.
Its use significantly improves operational efficiency and reduces the frequency of replacement, offering long-term cost savings. As a result, it has become a superior alternative to traditional materials such as steel wire ropes, nylon rope, and polyester rope.
UHMWPE mooring ropes are incredibly strong—7 to 10 times stronger than steel wire ropes of the same weight. This makes them perfect for handling heavy loads. They’re lightweight, easy to work with, and more reliable than nylon or polyester due to its low stretch, especially in tough conditions over the long haul.
With the same diameter, UHMWPE mooring ropes are 85% lighter than steel wire ropes, making them much easier for maritime workers to handle. This not only boosts mooring efficiency but also enhances safety for the crew. In comparison, nylon and polyester ropes are significantly heavier than UHMWPE ropes at the same strength level.
UHMWPE ropes have a longer lifespan compared to traditional fibers like polyester and nylon, thanks to their inherent abrasion resistance and low friction coefficient. The addition of specialized coatings further enhances their resistance to seawater, oil and UV damage. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements and operations, lowering labor and usage costs while helping protect the marine environment.

Nylon Mooring Line
Made from nylon material and are primarily used to secure yachts, sailboats, and large vessels. Due to their high strength, elasticity, and durability, they are particularly suitable for maritime applications. Their exceptional elasticity allows them to effectively minimize and absorb the impact forces generated by waves, strong winds, and vessel movements during mooring, thereby reducing damage to mooring points.
However, nylon ropes are prone to water absorption, which can slightly affect their strength in maritime activities. Prolonged exposure to water may also accelerate material aging, impacting their overall service life.

Polyester Mooring Line
Polyester mooring rope is a rope made from high-quality polyester fibers. It is widely used in marine operations due to its excellent abrasion resistance, high strength, lower stretch compared to nylon, and resistance to UV rays and chemicals. Additionally, the polyester rope‘s tensile strength and elongation remain unaffected even when wet, maintaining the same performance as in dry conditions. As a result, it is extensively applied in maritime activities such as dock and harbor mooring for vessels, offshore platforms, mooring buoys, and aquaculture operations.

Polypropylene Mooring Line
Polypropylene mooring rope is made from 100% polypropylene fibers and is commonly available in 3-strand twisted rope, 8-strand braided rope, and double-braided rope designs. Due to its lightweight nature, it is very easy to handle and use, reducing the difficulty of mooring operations.
Its ability to float on water has earned it the name “floating mooring rope”, as it helps avoid entanglement with underwater obstacles. Additionally, polypropylene rope is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it particularly suitable for marine operations.
Common applications include securing small vessels, anchoring mooring buoys, aquaculture, water sports, and rescue operations. However, in terms of strength and abrasion resistance, polypropylene is not as durable as nylon or polyester.
It is also prone to aging when exposed to prolonged sunlight. In dynamic mooring situations, its low elongation limits its ability to absorb shock. Despite these drawbacks, its affordability and low replacement cost make it a popular and widely used option.
Wire Mooring Line
Wire mooring ropes are ropes made from multiple strands of steel wire or other metals twisted together. They are known for their excellent tensile strength, low elongation, high durability, and long service life, making them particularly suitable for securing large cargo ships, oil tankers, and massive marine structures in offshore platforms, heavy-duty mooring, and anchoring systems.
However, compared to synthetic fiber materials, wire ropes are heavier, making them more labor-intensive to move and handle. Additionally, their steel construction makes them more prone to corrosion in seawater, requiring regular lubrication and maintenance, which increases costs. Their lower flexibility also makes them harder to coil and more challenging to operate, requiring higher operational expertise.
In some scenarios, high-performance mooring ropes such as UHMWPE mooring ropes have replaced wire ropes due to their lighter weight and easier handling. Nevertheless, wire ropes remain indispensable in heavy-duty mooring operations because of their superior strength and durability.
Types of Mooring Rope by Construction
Three-Strand Twisted Mooring Lines
Three-strand ropes are twisted into a spiral shape, making them simple and easy to splice and repair. They are commonly used as backups for small vessels or temporary mooring.
Double-Braided Mooring Lines
8 strand mooring rope is constructed with two braided layers: an inner core made of braided fibers and an outer braided protective cover. This design provides exceptional abrasion resistance while ensuring the tensile strength of the core, making them ideal for large vessels, long-term mooring at docks, and other applications requiring high durability and wear resistance.
Eight-Strand Plaited Mooring Line
Constructed with eight strands alternately braided, providing excellent anti-twisting properties. Due to their structural characteristics, they are less prone to tangling during deployment, making them particularly suitable for heavy-duty mooring scenarios in commercial shipping and offshore platforms where high anti-twist performance is required.
Twelve-Strand Braided Mooring Lines
Constructed with 12 strands braided in a circular pattern, typically in a single-braid structure, these ropes offer exceptionally high tensile strength and excellent resistance to twisting. They are well-suited for large vessels, heavy-duty mooring, and dynamic positioning systems.
Types of Mooring Ropes By Function
A proper mooring rope arrangement ensures that the vessel is securely fastened at its berth, preventing excessive movement caused by external forces such as waves, strong winds, and tides. Below are the types of mooring lines typically used in mooring arrangements:

Head lines
The head line is a mooring rope used to secure the bow of the ship. It connects the bow to a fixed point on the dock, ensuring that the bow does not shift or drift away from the berth due to strong winds, waves, or other external forces.
Stern lines
The stern line is a rope used to secure the stern of the ship. It connects the stern to a fixed point on the dock, ensuring that the bow does not shift or drift away from the berth due to strong winds, waves, or other external forces. It helps maintain the stability of the stern.
Spring lines
A spring line is a rope that connects the midship section of a vessel to a fixed point on the dock or berth. It is typically divided into forward spring lines and aft spring lines, and its primary purpose is to prevent the vessel from moving forward or backward due to currents, wind, or other external forces, thereby enhancing the stability of the vessel while moored.
Breast lines
A breast line is a rope that connects and secures the ship laterally to the dock. It is used to prevent the ship from swaying side to side while moored and to keep the bow from being pushed away from the dock by external forces, making it a crucial component of the mooring system.
Applications of Mooring Lines

Dock and Harbor Mooring
When a vessel is docked at a port or quay, mooring ropes secure the ship to the dock, berth, or bollard, ensuring that the vessel remains stationary during cargo loading and unloading, passenger boarding and disembarkation, or maintenance operations. This helps prevent the ship from drifting, reduces the risk of accidents, and ensures the safety of the crew. Typically, nylon or polyester ropes are used, but HMPE ropes are increasingly being adopted.
Anchoring and Buoy Mooring
Primarily used to connect vessels to buoys or anchor points, these mooring ropes help prevent the vessel from drifting due to water currents. Typically made of polypropylene mooring ropes or HMPE mooring ropes, they are also known as “Buoy Mooring Lines” or “Floating Mooring Lines” due to their excellent buoyancy. These lines are frequently used in fishing operations.
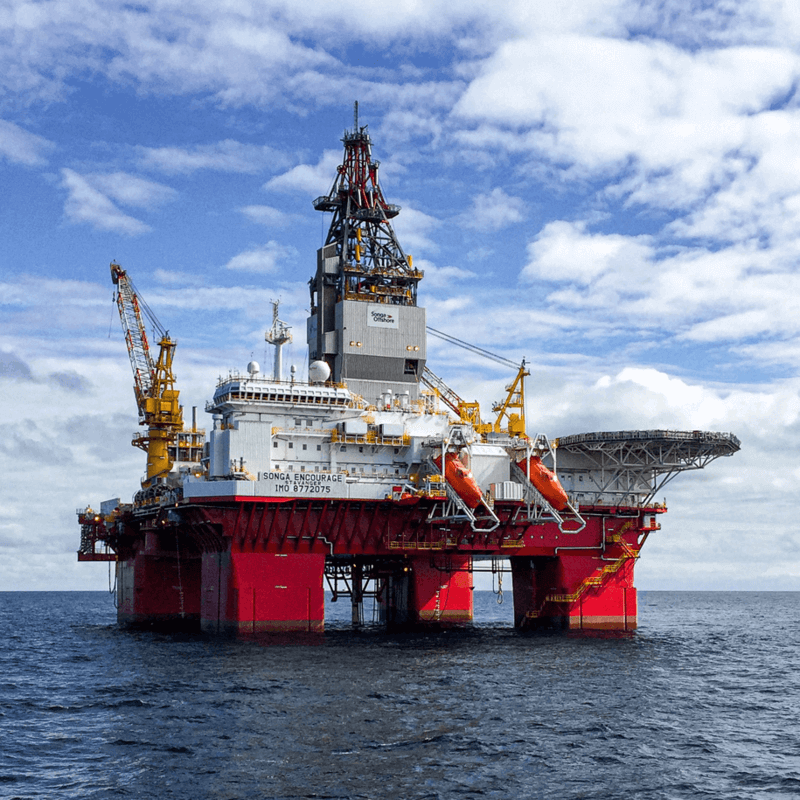
Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms
Since oil and gas platforms are typically located in open seas and deep waters, a stable system of mooring ropes is crucial for connecting vessels to the platform. Given the harsh and extreme environment, UHMWPE mooring ropes with a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent chemical and corrosion resistance, and low elongation are essential to support the platform’s regular operations effectively.
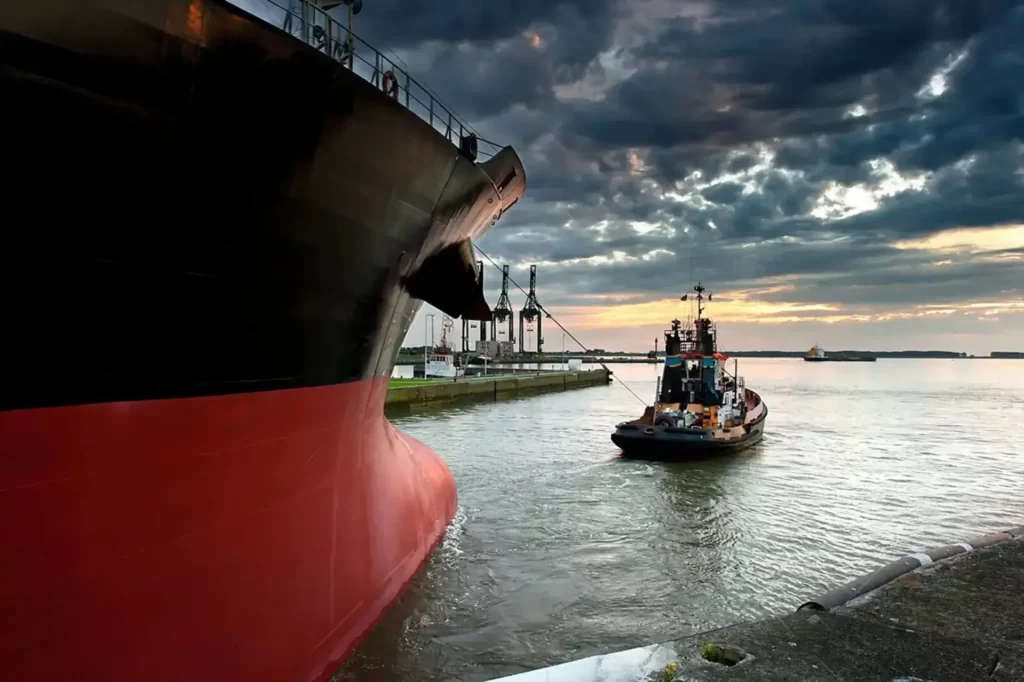

Towing and Salvage Operations
In towing and salvage operations, mooring ropes are used to connect tugboats with damaged vessels, stranded ships, platforms, or barges. Due to the immense pulling force required during towing, UHMWPE mooring ropes are widely used.
Permanent Mooring Systems
At yacht marinas, ports, and other long-term anchorage locations, mooring lines are used to provide vessels with stable and lasting mooring. Due to their low elongation, excellent corrosion resistance, and high durability, polyester and UHMWPE mooring ropes are recommended for use in these settings.
Key Considerations When Choosing Mooring Lines
Selecting the right mooring rope is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of maritime operations. Here are the key factors to consider:
Material
Mooring ropes are generally categorized into synthetic fiber mooring ropes and wire mooring ropes. Synthetic fiber mooring ropes can be further divided into UHMWPE mooring ropes, nylon mooring ropes, polyester mooring ropes, and polypropylene mooring ropes.
UHMWPE mooring ropes are renowned for their extremely high strength-to-weight ratio, lightweight nature, and low elongation. Nylon mooring ropes are known for their exceptional elasticity. Polyester mooring ropes are celebrated for their outstanding abrasion resistance. Polypropylene mooring ropes are characterized by their buoyancy, making them ideal for specific mooring operations.
On the other hand, wire mooring ropes are valued for their stable high durability and strength, making them particularly suitable for heavy-duty mooring applications.
Strength and Load Requirements
You need to evaluate and consider the weight of the vessel or object you intend to moor, ensuring that your mooring lines have sufficient breaking strength and working load strength to safely carry out mooring operations.
Stretch and Elasticity
When performing mooring operations, if you need to minimize the impact on the vessel and the dock, you should opt for high-elongation nylon mooring ropes.
However, if precise control and minimal movement of the moored object are required, low-elongation ropes such as UHMWPE ropes and polyester ropes are ideal. Among these, UHMWPE ropes offer the lowest elongation, typically around 3–4%.
Abrasion and Environmental Resistance
Given the harsh marine environment and the potential for wear and damage caused by friction between mooring lines, docks, and vessels, it is essential to choose highly abrasion-resistant ropes or add extra mooring line chafe protection to the eye splices at both ends of the rope.
Handling and Weight
Synthetic ropes, with their excellent flexibility, are particularly easy to handle during mooring operations, significantly improving efficiency.
UHMWPE mooring lines, in particular, stand out for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and lightweight characteristics. In contrast, steel wire ropes are heavier and less manageable, making them more suitable for mooring operations where frequent replacement or adjustments are not required.
Buoyancy
When performing mooring operations, if the mooring rope has buoyancy and can float on the water, it effectively prevents the mooring rope from becoming tangled with underwater obstacles.
Additionally, buoyancy significantly reduces the rope’s weight caused by water absorption, making it much easier to handle and move in deep-water mooring situations. Polypropylene ropes, with their density lower than water, offer excellent buoyancy and are also known as Buoy Mooring Lines.
Maintenance and Longevity
Although synthetic mooring ropes require less maintenance, their durability can still be enhanced by adding extra protection such as chafe guards or using double-braided constructions. This helps improve abrasion resistance and prevents degradation caused by prolonged exposure to UV rays and chemicals, thereby extending their service life.
Wire ropes, on the other hand, require regular lubrication and inspection to minimize corrosion and aging in harsh environments, ensuring their longevity. These measures are critical for the safety and reliability of mooring operations.
FAQ
What are the dangers of mooring ropes snapback?
When the tension on a mooring rope exceeds its breaking strength, the resulting snapback from the rope’s breakage can pose a serious threat to the safety of crew members or dock operators, potentially causing major accidents. It can also damage mooring winches or other equipment, leading to financial losses and disruptions to normal mooring operations.
Therefore, it is crucial to choose high-strength mooring ropes with an appropriate safety factor, conduct regular evaluations and inspections of the ropes, and designate a snapback danger zone. Additionally, operators must undergo strict safety training to minimize risks and ensure safe mooring operations.
how long should mooring ropes be?
Considering dock and tidal variations, as well as the different types and specific applications of mooring ropes, the length of a mooring rope is generally 1.5 to 2 times the length of the vessel. For example, if the vessel is 30 meters long, the mooring rope for the ship should be 45 to 60 meters.
what is the best rope for mooing lines?
The best mooring rope often depends on your operating environment, application, strength requirements, and cost considerations.
UHMWPE ropes, with their ultra-high strength, exceptional lightweight properties, and outstanding durability, are the most suitable choice for heavy-duty mooring applications. For general mooring operations, nylon ropes and polyester ropes are also excellent options.
What are mooring lines for recovery ?
Mooring ropes for recovery are specially designed ropes or cables used in emergency situations or challenging environments, such as retrieving vessels, objects, or equipment during grounding, capsizing, or drifting incidents.
These ropes are built to withstand high tension, heavy loads, and dynamic forces, making them an essential tool for maritime recovery operations and specifically tailored for these demanding scenarios.
Conclusion
We aim to use this article to help you gain a clearer understanding of the types, applications, and selection methods for mooring ropes, enabling you to make more informed and practical choices in specific applications.
As a professional mooring rope supplier and solution provider, Duracordix is committed to offering expert advice and customized solutions. If you’d like to learn more about our mooring rope size chart or have other inquiries, please feel free to contact us. We’re here to assist you!
About The Author

Moses Xu
Hi, I’m Moses Xu, VP and Marketing Director at Duracordix. With 10+ years in high-performance synthetic ropes and netting, I specialize in export trade and marketing. Whether it’s HMPE, Kevlar, or nylon ropes, I’m happy to share insights and connect!