Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Is your boat deck completely safe for every type of mooring operation? To maneuver your vessel and keep your crew safe, you need to know the procedures. This guide will cover the most important standards and equipment to assist you in mastering mooring, so keep on reading to ensure your next trips are as safe as possible.
What Is Safe Mooring Operation Procedure?
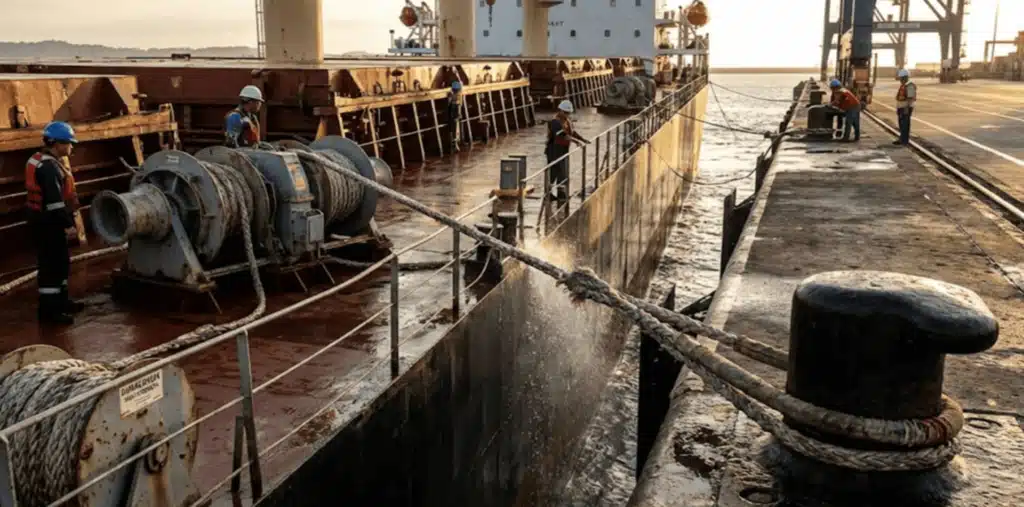

We need to define the specific mooring operation as the act of securing a ship to a sturdy land point. This process involves fastening the vessel securely to a specific mooring buoy or a solid pier structure. Therefore, this ensures that the ship does not drift away due to strong winds or changing water currents.
Consequently, the mooring definition means to temporarily hold a vessel fast against the external elements. However, you must not confuse this process with anchoring, because you are not using an anchor on the seabed. Have you ever felt the massive tension on a line during a storm?
Simply knowing the definition is not enough, because you have to understand the hazards of mooring operations to be safe. Furthermore, this procedure is a task that requires a specific set of equipment, like a mooring winch and bollards.
For a busy port, what is a specific mooring operation for the crew? Here, it is a combined effort of the ship crew alongside the receiving team on the land. It is essential to comprehend the mooring and unmooring meaning for total safety. The confusion that arises from moored vs docked is that mooring only relates to the securing lines.
When performing mooring a ship, you must use high-strength ropes like those made from Duracordix. The meaning of a standard mooring operation is to secure a vessel at sea safely. For instructions, a mooring operation pdf finds the steps in detail. A ship context mooring operation involves intense physical labor. The mooring operation on ship decks has high risks. This discipline is very strict for mooring vessel operations.
The Fundamentals Of Mooring Operation Explained Simply!
A. Critical Load Limits & Standards
Limits must be understood because these rules protect lives during every mooring operation. Therefore, standards like the meg4 will be explained below.
1. MEG4 Compliance
The meg4 guide is important because it determines rules of safety. Compliance is needed for safe mooring.
OCIMF Guidelines
The OCIMF issues the rules for mooring equipment, and compliance is necessary to stop incidents. The meg4 standard is stringent, so you must look at the Mooring System Management Plan. This plan protects safety, so you must look at the mooring lines to mitigate risks.
The guidelines are meant to protect the tankers, and SOLAS regulation ii 13 8 requires this compliance. The Mooring Arrangement Plan fits here, and the Mooring Arrangement Diagram illustrates the plans.
ISO 2307
This standard is for the testing of ropes, and it examines the strength accurately. Accurate information is a must because the marine mooring equipment is dependent on it. You assess the elongation, and ISO 2307 describes the methods of testing. You authenticate the Minimum Breaking Load for the quality assurance. Duracordix does this, so you can be assured of the results of the test.
Class Approval
Ship classification societies review and approve certain technologies for ships, so you check their certificates. This regulation is important, and the mooring equipment list is subject to your own approval. The class surveyor checks your equipment and gives you a certificate that proves you are legal and safe to operate. The mooring operation equipment list is provided for the mooring operation equipment that is for sale.
2. SWL Calculations
Loadings are calculated carefully to prevent line breaks and to ensure that the rope can handle the needed stress.
1140kN MBL
A standard 40mm HMPE rope is very strong, and it can hold 1140kN of force. This limit is known as the ship design MBL, and you must never exceed this specific break point. It should be easy to find the ship design MBL if you check the certificates because it is used to secure the ship.
50% Break-force
A safety margin needs to be used to determine the working load. It is 50% of MBL and is intended for safe mooring operations. You must avoid an overload, and the mooring rope size guide is extremely helpful in selecting the right rope. Therefore, you keep the tension low to prevent sudden failures.
Safety Factor
You need a buffer because moisture absorption and wear are accounted for. Ship mooring depends on it, and a 2:1 safety factor is common and reasonable. Environmental and external forces acting against the mooring are accounted for in the mooring equipment design philosophy as well. You plan for gusts because extra safety always goes a long way.
3. Bending Ratios
15:1 D/d: A 15:1 ratio is a must to protect the mooring equipment as well as to ensure it works within its designated lifespan.
Sheave Diameter: The sheave must be big because small sheaves are on the mooring equipment damage list. You must ensure a reasonable sheave size.
Fiber Compression: Tight bends crush fibers, so you can assume the marine mooring equipment suffers. This is why tight turns should be avoided.
B. Snap-back Zone Management
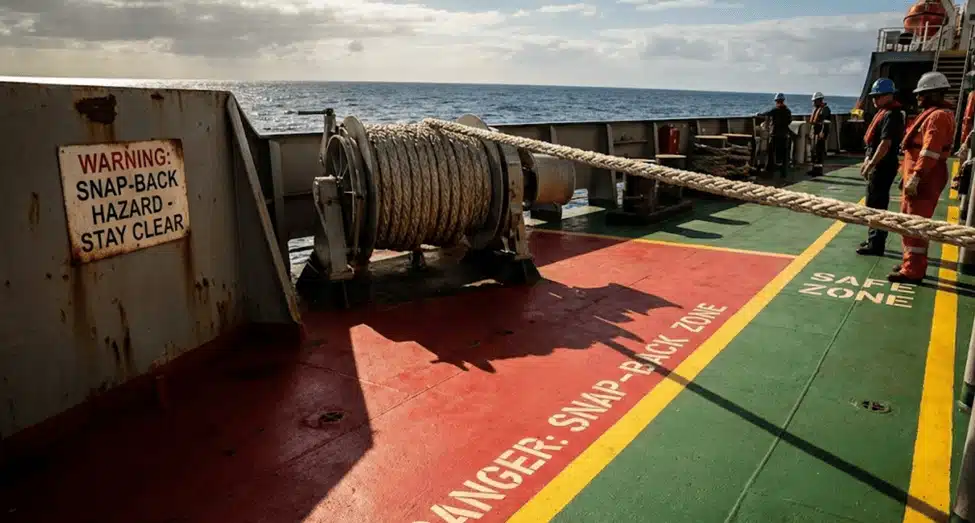

A broken rope is a deadly weapon, and this is the primary reason for identifying the red zones on deck.
1. Kinetic Recoil
Rope stores energyand releases it quickly, so this is what you need to learn about recoil during breaks.
80% Less-recoil
HMPE ropes are inherently safe because they possess 80% less recoil. This means snap back zone risks are largely mitigated. The rope simply falls down, and it does not whip back. Mooring operation accidents are reduced as a result. Choosing Duracordix HMPE effectively protects the crew where a small snap back zone is present as well. The mooring operation is simply safer.
20% Nylon- Stretch
Nylon rope is unique because it can stretch a lot, up to 20% to be exact. This can be stored, and it has huge energy stores. A break can lead to deadly consequences, so there is an increased risk of mooring operation hazards. So be careful, because the rope behaves like an old-school rubber band. Be mindful because the operational mooring rope rubber band risks are high.
Stored Energy
Energy is created when tension is built, and this increases hazard in mooring and unmooring operation. Having a map is important because it helps you visualize potential dangers. The risk in mooring operation is very real. You need to release tension gradually to avoid sudden breaks. The energy must be managed as it can be deadly.
2. Danger Zones
This is where you paint the deck, and the crew are instructed on where to safely stand. This visual aid prevents fatal accidents on the vessel.
Red Painting
A deck painted red is an easy warning sign because it identifies the danger zone. This provides clear guidance as to where the safe zone is during mooring operations. The danger of being uncomfortably close to the mooring operation hazards is clear, so you stand outside the red zone.
Visual Alerts
Through the using of signs, the crew can easily be made aware of the operational hazards. These visual aids, and the training of your team, helps avoid mooring operation hazards. Visual aids can save lives, so you stay alert. “The Swedish Club warns, ‘Snap-back zones are complex and can change depending on the mooring configuration.” Mooring unmooring operation hazards are marked.
Stand Clear
You do not stand in loops because mooring operations hazards are fatal. You keep distance because the rope can slip. You stay out of snap back zone, and you watch the line. And you are safe, so you go home.
3. Crew Safety
You have wearable and non-wearable protective gear, and we have a list of essential items for you.
Impact Gloves
This is one of the keystones of mooring operations safety procedures. You wear impact gloves because they protect hands. You handle ropes cautiously to avoid crushes. Your hands are safe.
Non-slip Boots
You wear non slip boots because the deck is wet. Safety precautions during mooring operations list boots. You do not slip, and you stand firm. You work safely, so fewer accidents happen. You are stable.
Hard Hats
A hard hat is also required because falling gear can injure your head. They are a requirement for mooring operations for safety purposes. You wear it tight, and you follow the rules. The head is vital, so you protect it well.
C. Winch Operation & Braking
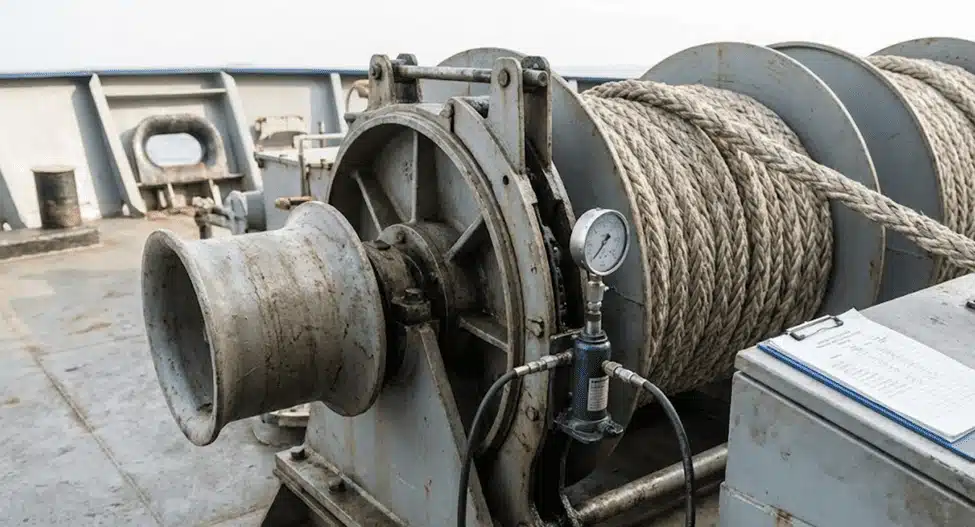

The winch is what holds the ship, and the brakes are the most important. You must check and test them often.
1. Holding Capacity
Brakes hold the load, so you set them right. We explain the holding capacity limits below.
60% MBL
Set brakes to 60% MBL because this is the limit. Mooring winch operation relies on this. The brake holds tight, and mooring winch brake test confirms it. You prevent slippage, so the ship stays put. You are secure.
Rendering Point
The brake must slip, and it slips before breaking. Mooring winch maintenance ensures this. You protect the rope because mooring winch parts must work. You avoid damage when the line pays out. The ship is safe when mooring winch safeties activate.
Brake Testing
You test brakes yearly, and you use a jack. Hydraulic mooring winch operation needs checks. You verify force, and self-tensioning winches on auto mode need care. As INTERTANKO advises, “Winch brake testing kits must be used annually to verify holding capacity.” You record results, and the brake is ready. You trust the gear.
2. Drum Spooling
Spooling affects the rope because bad layers cause damage. You learn to spool lines correctly.
Split Drums
Mooring operation step by step lists this. You store the slack.
1 Layer
One layer is activated, so this is less cutting. Operations of mooring lines are smooth. Lines of mooring sit flat, and fibers are protected. This is recommended by Duracordix.
Tension Control
Tension is controlled by spooling tight because operations of mooring lines need care. Loose turns bite in, so back tension is applied. The drum is neat and safe, and knots are avoided.
3. Heaving Speed
15m/min Rate: Heave at 15m/min because this is safe. Mooring operator reverse.
Slow Start: Start the winch slowly.
Controlled Pay-out: You pay out smoothly because line handling training reduces risks. You use less control when the line feeds out. You are skilled.
D. Environmental Force Dynamics
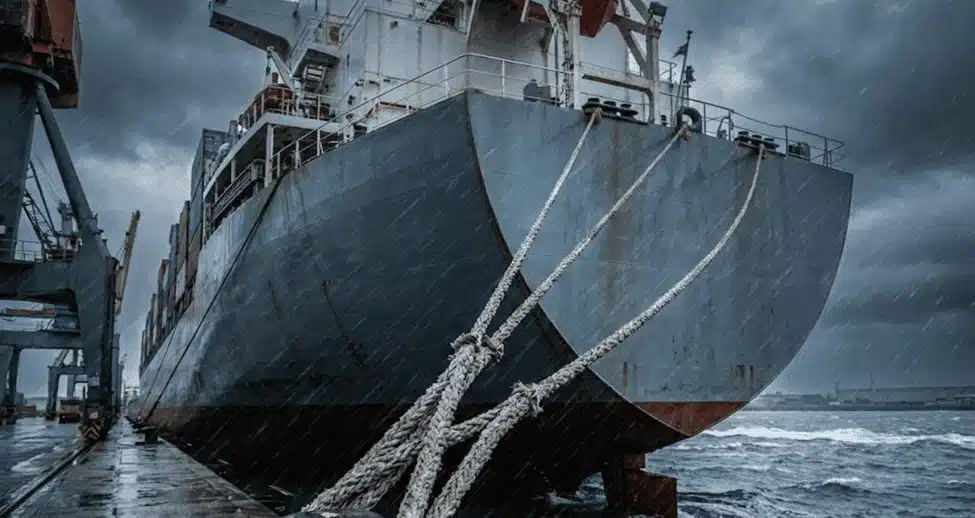

The ship has to combat these elements, so calculating these forces is crucial for safety.
1. Wind Loads
The ship is susceptible to the wind push on the hull, and the gusts can be hazardous. The windage area is critical for your calculations.
60-knot Gusts
Wind can hit up to 60 knots, and the force escalates at high rates. During mooring operations on a well-managed vessel, you must prepare for the gusts. These mooring operations struggle to be safe. You must add lines to the vessel and hold the ship in place for safety. The COSWP emphasizes, “A risk assessment must be carried out before any mooring operation commences.”
Lateral Force
Wind hitting the side of the ship is classified as lateral force. This is accounted for in the risk assessment for mooring operations. The ship can begin to drift, and this is predicted by the risk assessment for mooring operations. You deploy breast lines to stop the ship’s drift.
Windage Area
The hull of the ship catches the wind and creates a windage area. This area is calculated by the risk assessment for mooring operations template. Tall ships catch more, so you require good lines. You plan early because the vessel must be secured.
2. Current Effect
The ship is also affected by the push of water because the currents can be strong. You must check the under-keel clearance for drag.
3-knot Drag
A 3-knot current can be quite strong, and it can drag the ship well. This must be accounted for in mooring and anchoring operations. The drag increases the force on the vessel. During mooring and anchoring operations, spring lines must be used. You can stop the ship from moving.
WD/T Ratio
Examine the WD/T ratio because drag increases with shallower water. This increases difficulty and risk of the ship to ship mooring operation. Brace yourself, so you must calculate the depth. Adjust your mooring lines and stay safe.
Underkeel Clearance
Low clearance obstructs water flow, increasing the force that pushes the hull on the current. You must watch the tide and adjust your mooring lines for the safety of the ship. It is physics, so you know how to moor securely.
3. Static Balance
The ship must stay still, and forces should be equal. You know how to balance the mooring lines exactly.
Equilibrium State
The ship stays still when the forces become still. These are steady forces. You have arranged the mooring lines in a way that aids the layout of the ship in order to eliminate the wind and the lines. The ship is still, so you have obtained balance.
Restoring Forces
The lines are restoring, so the ship moves with the lines. The rope tightens and becomes taut. The stability of the mooring itself is the most important. You have trust in the system.
Symmetric Arrangement
You arrange the lines in a way that they are spooled evenly, creating symmetry. The load is evenly distributed. If a line does break, the others will be intact and you will be safe. You have a good working system, and Duracordix will advise you to use this equal symmetric arrangement.
E. Line Connections & Geometry
The strength of the system is affected based on the angle of the lines. You are able to rig the lines for max hold.
1. Mooring Tails
Tails allow for some lift, and they guard the wires from chafing. You join them to absorb shock loads.
11m Length
Because they have good stretch, it is best to use 11m tails. They are used with mooring lines during operations. Wires are stiff and tails absorb the shock. This is what the mooring operation procedure tells you. You connect them, and the system has a longer lifespan.
22m Pendants
If you have exposed berths, longer is better. 22m is the length recommended in the mooring operations manual. 22m is better for exposed berths because the waves can move the ships. Long tails are able to stretch, so some tails are included in the mooring operation safety. They minimize peak loads, and this is a safer option.
Cow Hitch
You use a cow hitch to join them because it is secure. The safe mooring operation guidelines allow for this. Do not use shackles as they will cut the fiber, because the cow hitch is strong and will just do fine. This is a knot that you would want to have a look at, it performs good.
2. Deck Fittings
Fittings guide the rope, while smooth surfaces prevent cuts. You inspect chocks and fairleads.
Roller Fairleads
Rollers guide the rope, and they are used for reducing friction. Deck fittings and mooring equipment, like fairleads, have rollers that must spin. They are in the mooring deck and need to be greased. So, the rope can move freely, and not chafe, fairleads need to reduce friction.
Closed Chocks
Chocks that keep the line enclosed are closed chocks. They are at the mooring station along with other chock components. They are enclosed so that the rope stays in. With closed chocks, equipment at the mooring station becomes essential. You have to examine the chocks for a smooth surface. They have to be smooth, so they can’t have sharp edges. The mooring station definition is obvious.
Smooth Surface
Keeping surfaces smooth is essential to prevent ropes from getting cut. You need to keep mooring line stoppers clean. The short mooring post needs painted, and the mooring station equipment needs looked after. You need to sand rust to protect the rope.
3. Lead Angles
Angles reduce strength, so keep lines straight. You manage the vertical and horizontal leads.
25-degree Maximum
Keep angles low because the max is 25. This is stated in the procedure for mooring operations. High angles cut the strength. This is a warning in the procedures of safe mooring operations. You move the ship, and you align the line.
Vertical Dip
This is vertical dip, so look at the line. Mooring and unmooring operation procedures check this. Steeper lines hold less. Mooring and unmooring operation procedures equipment and reporting notes it. The trim is adjusted by you.
Parallel Run
Spring lines run parallel because they stop surge. Breast lines run straight because they stop sway. You align for maximum hold, which is what you want. It is the working geometry, so the ship is secure.
F. Inspection & Retirement Criteria
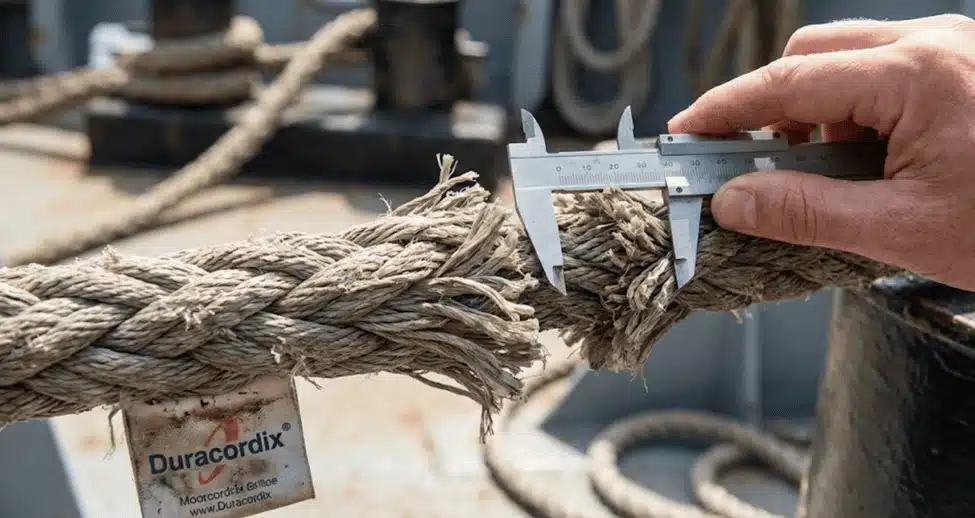

You look and see ropes get old. Damage line retirement is what we explain below.
1. Wear Limits
Rope gets damage, so you measure the wear. Limits define retirement.
10% Reduction
Diameter-shrinking limits are 10%. Why items of mooring equipment should be inspected before a mooring operation is obvious. Mooring equipment failure happens. You measure, and you discard it. The Samson Rope states, “Regular inspection is the best defense against unexpected line failure.” Thin ropes break.
Strand Volume
Look at strand volume, and if worn, replace. Mooring equipment mass function is determined. You see flat spots. Used mooring operation equipment fails. You change the line.
2. Service Life
All fibers deteriorate over time, and ropes lose integrity from UV light. Keep track of age and usage cycles.
5-Year Cap
Retire the line after only 5 years because you can’t even use it this whole time. Mooring operations pdf states this. Time weakens fibers. You check the tag, and you buy new. Your supplier is Duracordix.
Cycle Testing
Fatigue breaks ropes, and heavy use deteriorates it faster. Operations for mooring ppt states this. You count cycles. Mooring operations training teaches this. High traffic kills the fibers in a rope.
Residual Strength
Test old ropes because ship mooring training gives this advice. You know the truth when we send a sample and the lab tests it. It fails on the lower end of the desired break strength, so you replace the fleet.
3. Protection Gear
Chafe Guards: You use chafe guards, and you put them in chocks. You need them for safe mooring operations. Friction kills rope. They slide on, and the rope is left unfrayed.
Polyester Sleeves: The sleeves protect the lines from abrasion because the polyester is strong. Mooring operations on ship all use sleeves. They are cut resistant. The mooring and unmooring operations are safe. You Velcro them to the line.
Leather Sheath: Leather will protect your eyes while you sew. The splice is weak, and leather helps. It stops cuts and rust, and the eye will last longer. You really are smart.
Common Types Of Marine Mooring Systems!
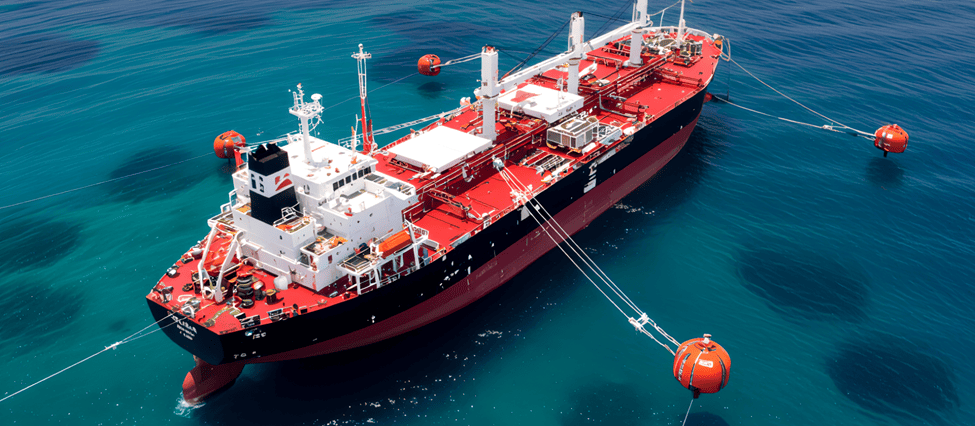

Single Point
A single point mooring buoy is stationed offshore. This system allows the ship to freely weathervane. Single point mooring operations mitigate wind and wave forces. Tankers are used for loading oil. The single point mooring maintenance and operations guide is critical. The bow is connected to the buoy.
Spread Mooring
You are fastening the vessel with several anchors, which comes with different patterns. This system keeps the vessel on a fixed heading. This is used for drilling rigs. Different types of mooring operations require precision, and this one is no different. It sustained forces from all directions.
Catenary Systems
The weight of the chain is relied on. Heavy chains form a curve called a catenary. Different types of mooring operations use gravity to restore. The chain rests on the seabed. Various systems for mooring use this in shallow water. It offers the system flexibility.
Conventional Systems
The water depth and seabed traits must be considered to gain optimal mooring system performance.
Chain Systems
Heavy chains are used to hold a position. The depth of the water must be considered for optimal performance.
Taut Rope Systems
A rope is used, and it is always stretched. The rope is always submerged in the water. It must be kept flat.
Taut Leg
Here you adjust the horizontal load right above the deck, and arrange vertical line on the winch drum so the seabed footprint is small. Equivalent to Mooring Operation – Deep Water type, this is where Duracordix HMPE is used. It dampens the vertical motion of the ship. The lines are always under extremely high tension on the order of several hundreds of kN.
Mediterranean Moor
Here you bring the Stern to the quay, and then you lower the bow anchors. Mooring operation type used in crowded ports to efficiently save space on the quay. The 4-point mooring procedure is used, and this requires a high level of skill to execute.
Baltic Method
This is used when the high wind situation is onshore. You put out an anchor to hold the vessel off. Mooring operations are adapted according to the situation in a given weather. This prevents the ship from crushing the fenders. The technique used is the anchor berth technique. It offsets the wind force.
Running Moor
Release an anchor while moving at a moderate speed. Then, a second anchor is dropped. Mooring operation types use this for increased control and to vastly smaller the swing radius. It keeps the vessel steady. Boat mooring systems use varying adaptations of this.
Standing Moor
Release the port side anchor first. You drift back and release the starboard. 4-2-2 mooring arrangement concepts apply here. It is similar to the running moor. The mooring capstan operation is used to adjust the tension. It allows for a steady position.
| System Type | Primary Application | Restoration Force Mechanism | Heading Control | Seabed Footprint | Typical Components |
| Single Point Mooring (SPM) | Offshore Oil Loading (Tankers/FPSO) | Buoyancy & Hawser Tension | Weathervaning (360° Free Rotation) | Minimal (Anchor Radius) | Buoy, Hawsers, Anchors, Swivel |
| Spread Mooring | Drilling Rigs, Semisubmersibles | Anchor Line Tension | Fixed Heading (Stationary) | Large (multi-anchor pattern) | Anchors (4-12+), Chain/Wire Lines |
| Catenary System | Shallow to Mid-Depth Platforms | Gravity (Weight of Chain Curve) | Variable (Depends on arrangement) | Large (Requires scope for curve) | Heavy Chain, Drag Anchors |
| Taut Leg System | Deep Water Operations | Elastic Rope Tension (Vertical) | Fixed/Stationary | Small (Vertical loading) | Polyester/HMPE Rope, Suction Piles |
| Mediterranean Moor | Crowded Ports/Marinas | Stern Lines & Bow Anchors | Perpendicular to Quay | Minimal (Quayside) | Stern Lines, Bow Anchor |
| Baltic Moor | Quayside with Onshore Winds | Anchor & Shore Lines | Parallel/Angled to Quay | Moderate (Requires standoff) | Offshore Anchor, Stern/Bow Lines |
| Running Moor | Tidal Rivers/Streams | Dual Anchors (Sequential Drop) | Restricted Swing Radius | Moderate (Linear spread) | Two Bow Anchors (Port/Stbd) |
| Standing Moor | Long-term River/Tidal Berths | Dual Anchors (Fixed Spread) | Steady Position | Moderate (Linear spread) | Two Bow Anchors, Capstan Tension |
Comparison of Marine Mooring Systems and Operational Characteristics!
HMPE Vs Wire: Best Mooring Line Materials!

High Modulus
Choose HMPE if you want high modulus properties. It stays nice and stiff like steel wire. This stiffness benefits the mooring operation equipment list. It also effectively limits vessel drift. Better user control is offered in these ropes. You can choose from rope products like Duracordix.
Low Elongation
You can count on low elongation in the 3-4% range. It also remembers the exact profile of steel wire. Low stretch is highly recommended and specified in mooring equipment guidelines for this reason. It prevents the rubber band effect. This is also why the vessel stays fully and effectively in position.
Specific Gravity
Benefit from the 0.97 specific gravity. HMPE ropes and lines float on water surfaces. The ship mooring operation also becomes easier with floating lines. Wire ropes sink and get dragged. This is why mooring operations meaning includes “ease of handling”. Floating lines also avoid props.
UV Resistance
Get with Duracordix superior UV resistance. During mooring operations on ship, exposed ropes are in constant UV light. Less sunlight degrades UV ropes. Wire ropes also don’t suffer UV damage. UV loss also gets special consideration in a mooring rope size guide. Some coatings also protect the fibers from UV sunlight.
85% Lighter
Handle ropes that are 85% lighter. This has a quick and direct impact in reducing crew fatigue. Mooring lines operations are faster with HMPE. Heavy wire ropes require lifting gear which just complicates things. Lighter ropes are just better. It also makes manual handling safer. DNV notes, “High-modulus synthetic fiber ropes offer weight savings and ease of handling compared to steel wire.”
Cyclic Tension Load Management
You must manage tension cyclic loading because mooring operation equipment endure repetitive stress. Cycles are worse than wire suffers metal fatigue. Mooring equipment fatigue life guidelines help improve resistance.
Tensile Fatigue
Monitor tensile fatigue damage over time. During the ship mooring operation, constant tension cycles occur. Duracordix wire breaks after fewer cycles. Mooring operations meaning durability translates to monetarily saving long economic life.
Corrosion Immunity
Rust must be eliminated with synthetic rope because wire rope corrodes. Designed for ship mooring operations, wire rope degrades with salt water spray. Duracordix ropes are immune to corrosion. Mooring rope size guide includes loss to moisture.
Creep Rupture
You must manage the permanent under load from moisture creep rupture. Mooring lines with rope wire do not creep. Mooring equipment list must include creep limits. Choose the right grade.
How To Calculate Mooring Line Tension Accurately?
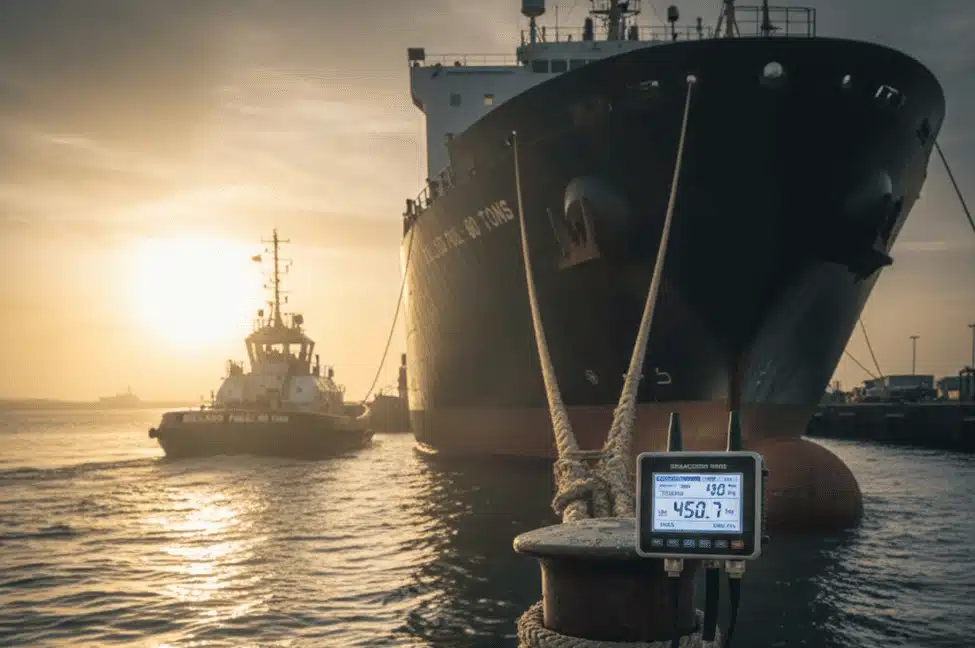

Pre Tension Loads
Set 10% MBL during communications for mooring operation slack removal. Mooring hand signals guide the winch operator. Proper pre tension load balancing avoids optimum shock loading.
Working Load
Find the Safe Working Load limit. You keep the loads below 50%. Mooring operation hand signals assist in adjusting the tension. When can an operator moor his vessel to a signal that involves these limits? You watch the winch gauge.
Safety Factor
Apply a safety factor of 2.0. What are the 6 steps of safe mooring operations that include this calculation? It offers a safety margin. When can the operator of a pleasure craft moor depends on safety. You factor in the wind.
Elastic Stretch
Calculate the elastic stretch percentage. During a mooring operation communications equipment helps monitor stretch. You predict the vessel motion. Mooring hand signals indicate stop or go. The stretch affects the position.
Load Cells
Read information from digital load cells. Mooring operation hand signals confirm the readings. Load cells give real-time tension. When can an operator moor his vessel to a signal? It is safer with data. You mount them on pins.
Dynamometer Readings
Use a dynamometer for line tests. What are the 6 steps of safe mooring operations that include testing? You clamp it on the line. When can the operator of a pleasure craft moor safely? When the tension is known. It confirms the load.
Bollard Pull
Most of the time, the required bollard pull is calculated before the ship arrives at the port to do the mooring. During a mooring operation communications equipment coordinates tug boats, and you then match the required power of the tug. For mooring hand signals guide the tugs, and the pull should match the wind forces.
Breaking Strength
You are aware that there is a Minimum Breaking Strength (MBS). During a mooring operation hand signals are used to warn others of the high tension, and you never break that limit. When can an operator moor his vessel to a signal in a safe manner? Below the breaking point. This data is available in the charts.
Integrated Monitoring
Employ an integrated tension monitoring system. What are the 6 steps of safe mooring operations that include monitoring? Alarms sound at high tension. When can the operator of a pleasure craft moor with technology? It automates safety. Duracordix is one of the many companies that supports smart systems.
| Parameter | Target Metric | Measurement Device | Operational Function | Critical Limit | Monitoring Method |
| Pre-Tension Loads | 10% MBL | Winch Brake | Slack Removal | >15% MBL | Hand Signals |
| Safe Working Load | <50% MBL | Digital Load Cell | Static Holding | 55% MBL (Max) | Winch Gauge |
| Safety Factor | 2.0 Coefficient | Design Calculator | Weather Buffer | <1.82 (MEG4) | Risk Assessment |
| Elastic Stretch | 3-20% (Mat. Dep.) | Strain Gauge | Motion Prediction | Yield Point | Comm. Equipment |
| Bollard Pull | Wind Force Equiv. | Dynamometer | Transverse Thrust | 100% Tug MCR | Tug Coordination |
| Breaking Strength | 100% MBL | Tensile Data Chart | Ultimate Failure Point | 1140kN (Example) | Cert. Review |
| Integrated Monitoring | Real-Time (ms) | Smart Bollard Pin | Automated Alarms | Alarm Setpoint | Bridge Display |
Mooring Operation Tension Calculation and Load Limits Technical Matrix!
Future Trends In Mooring Operation Technology 2025!
Automated Winches
You do use automated vacuum mooring systems. Mooring operation ship processes become completely hands-free. Robots are the ones to attach the lines. Mooring operation training shifts to software. It brings crews out of dangerous areas.
Magnetic Berthing
Dock with powerful magnetic pads. Safe mooring operation training is also educative with magnets. Ropes are not needed. 6 types of mooring equipment now include magnets. It holds the steel hulls firmly. The release is Instant.
Vacuum Mooring
Ships are secured using specialized vacuum pads. Each mooring system management plan includes vacuum units as they remove any risk of snap-backs. This mooring operation improves safety to the ship being moored and it only takes a few seconds. Duracordix is the only company with the technology to monitor this in real-time.
Load Sensors
Rope systems used in mooring are embedded. Sensor data during mooring operations training and real-time visible data during training helps highlight areas where safe mooring operations can be enhanced. Work management systems used by Duracordix predict failure early which is a valuable capability and are currently researching smart fibers that are embedded into mooring systems.
Smart Bollards
Bollards with installed load cells are placed shore-side. These integrate and enhance 6 types of mooring equipment to be smart. They measure and monitor the line tension on shore-side. This information can be used from an integrated mooring system management plan to inform port operators on the loads in use and warnings of when an overload is imminent are alarms triggered by the system.
Real-time Data
You can view data that shows the current tension on the rope in real-time from a tablet. Data-driven decisions can be made by the ship’s captain when mooring operations are in use. Data from mooring operations training is used for educational purposes during training to enhance the captain’s decision making to maximize safety and efficiency in the operation. Dashboards are used during safe mooring operation training to enhance efficiency and safety during the mooring operation.
Digital Twin
You simulate that mooring operation using digital twins to avoid the risk of damaged equipment and simulate 6 types of mooring equipment that have been virtually modeled. These managed simulation systems identify and use to optimize systems to predict maintenance.
Bio-Synthetic Fibers
These are the new eco-friendly bio-based ropes that are used in mooring operations. These new ropes sustain the ship to complete operation training while enhancing the sustainability of the mooring operation. Duracordix is the company that leads innovation to integrate green technology.
Instant Unmooring
You utilize remote quick-release hooks. 6 types of mooring equipment contain QRH. You delete lines within moments. QRH is required by the Mooring System Management Plan. Fast terminal emergency departures. It improves terminal safety.
FAQs – Bonus!
What Is The MEG4 Standard For Ropes?
Special MEG4 rope standard states that a minimum safety factor of 1.82 must be placed on synthetic rope. It also requires a line of rope management and extensive testing. Duracordix ropes are compliant to these OCIMF standards.
How Does Catenary Depth Affect Anchor Holding?
The catenary depth increases the horizontal pull on the anchor during a mooring operation. Less of a pull means the anchor flukes can dig in more. Insufficient scope can cause drag by lifting the anchor.
Why Use Synthetic Tails With Steel Wire?
When mooring tails are added to wire ropes, they introduce additional elongation that absorbs shock loads. They provide a reduction of the peak dynamic tension that is created by waves. Tails prevent wire from snapping during a surge if a line is fast to a vessel. As noted by the Nautical Institute, “Synthetic tails are essential for absorbing peak loads in wire mooring systems.”
What Defines A Snap-Back Danger Zone?
The snap back area is the area where a rope that fails will snap back and recoil with potentially deadly force. These areas are wide due to the potential for deflection of ropes across structures like bollards and fairleads. Stay out of these areas with red lines.
How To Calculate Minimum Breaking Load MBL?
Ship design MBL is calculated according to the vessel’s windage area and equipment number (EN). Represents the maximum force the mooring system must endure. You can find this value in your ship construction certificate. “Where to find ship design MBL? Check the Mooring Arrangement Plan.”
Difference Between Taut Leg And Catenary Mooring?
Types of mooring differ; taut leg systems use vertical tension for stability in deep water, while catenary systems use the weight of the hanging chain to regain position. Taut leg systems do, however, have a smaller seabed foot print.
What Is The Safe Working Load SWL?
SWL is the maximum load a rope can have without risk of failure during safe mooring operations and is typically 50% of MBL. Exceeding this limit can cause the rope to fail which is why this value is used, to give a safety margin. Exceeding this can cause the rope to break and fail.
How Does Windage Area Impact Mooring Force?
Larger windage areas tend to catch more wind which increases the hazards of mooring operations, thus requiring stronger mooring lines and more to hold the vessel. Ballast conditions often increase the exposed windage area, and the hazards that come with it.
Why Is The 15:1 D/D Ratio Critical?
This ratio is the most important because it prevents internal heat from forming, which in turn, prevents fiber crushing in the equipment used for mooring. Having a sheave diameter 15 times the rope diameter ensures that the equipment will last a long time. Tight bends in the rope can weaken it, and this is especially common with the mooring equipment.
When To Retire Damaged HMPE Mooring Lines?
Retire the line when mooring line operation inspections show 10% diameter reduction, fused fibers, cut strands, or severe abrasion. These are grounds for immediate retirement. Regular visual checks are essential.
What Is The Function Of A Fairlead?
Deck fittings and mooring equipment, such as fairleads, guide the rope to the winch. They stop chafing against the ship’s structure. Roller fairleads also help mooring equipment and winches by reducing friction when line pay-out occurs.
How Do Spread Mooring Systems Maintain Position?
A mooring arrangement of spread mooring systems holds the vessel with anchors from multiple directions. This restricts movement and keeps the heading of the vessel fixed. It is stable but cannot weathervane unlike single point mooring systems.
What Are The Benefits Of Single Point Mooring For Tankers?
With single point mooring operations, a tanker can rotate with the wind and waves, minimizing the environmental forces on the hull. It also allows for safe offshore loading in rough weather. “The SBM tanker mooring operation is designed for flexibility.”
What Causes Shock Loading In Mooring Lines?
Shock loading occurs when there is sudden movement of the vessel. This can lead to mooring operation accidents. Large forces are generated by slack lines that suddenly snap tightening. To avoid this dangerous spike, pre-tensioning lines need to be used.
How To Prevent Chocking In Mooring Operations?
Proper line handling techniques avoid handling rope that become jammed in winches or chocks. Ensure smooth spooling on the drum. Maintain tension to avoid loose coils that become bound.
Conclusion
Total safety onboard is possible if you follow the guide given for your vessel. A complete understanding of the mooring operation is necessary to protect your team, so implement these safety changes. Quality gear should not be compromised, so visit DURACORDIX for excellent alternatives. The best protection of your crew is a priority.
About The Author

Moses Xu
Hi, I’m Moses Xu, VP and Marketing Director at Duracordix. With 10+ years in high-performance synthetic ropes and netting, I specialize in export trade and marketing. Whether it’s HMPE, Kevlar, or nylon ropes, I’m happy to share insights and connect!