Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Do you need to securely moor your ship? You can find the right rope with this guide. We will talk about various mooring lines for ships. We explore different materials and how ropes are made. With this information, your vessel will stay safe, moreover, your crew will be secure during the entire mooring procedure.
What Distinguishes The Various Types Of Mooring Lines For Ships?

The different mooring lines for ships are designed for your vessel’s specific needs. Every feature is important for your safety, for instance, the materials can be different. They can also have different constructions and purposes. The breaking strength and the line’s stretch are both very important.
Synthetic fiber ropes offer you great advantages. So, choosing the right mooring lines for ships for any job is critical. This will help you secure your vessel safely. That is the true mooring line meaning.
Exploring The Core Types Of Mooring Lines For Ships!
In the next sections, you will learn about the main type of mooring lines. We will look at their functions, materials, and constructions to give you a full picture of the types of mooring lines for ships.
A. Mooring Lines By Onboard Function

Let’s first look at how lines are used on a ship. The location and job of each rope are very important for a good mooring.
1. Head lines
Description
A head line is a very important mooring rope. You use it for mooring a ship by securing its bow. It is a key part that ties the ship’s bow to a spot on the dock. This keeps the moored ship from moving away and helps with the berthing and unberthing operation of a ship.
Why It’s Better?
The head line stops the bow from moving away from the berth. This feature is very helpful for the front of the boat. It protects it from shifting because of strong winds and waves. Therefore, it is a key piece of mooring equipment.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Uses bow cleats to tie off
- Prevents the vessel from drifting
- Secures the bow of the vessel
Critical Applications
- Dock and harbor mooring
- Berthing operations
- Securing against side-to-side currents
2. Stern lines
Description
A stern line is the rope you use to secure the stern. You can think of it as the line that moors the back of the vessel. It holds it from drifting backward, which is the stern line definition. Using a quality shipping rope here is vital.
Why It’s Better?
With a stern line, it is much easier for you to control the back of the vessel. This means the stern will not swing out into the open water. This control is a vital part of keeping your vessel safe. Ultimately, a good ship mooring rope makes all the difference.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Keeps the stern in position
- Uses cleats at the back of the boat
- Secures the vessel’s stern area
Critical Applications
- Long-term docking and mooring
- Loading and unloading cargo
- Ship mooring and unberthing
3. Spring lines
Description
A spring line and breast line setup is common. The spring line connects the middle part of your vessel to the dock. It holds the vessel still, so it cannot move forward or backward. It is one of the most vital lines in a mooring arrangement. It is a key part of what is mooring a boat.
Why It’s Better?
Using a spring line greatly improves the stability of your moored boat. It is essential to fight the push and pull from passing ships. This is a key difference in the mooring vs docking debate.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Controls forward and backward movement
- Includes a forward spring line
- Also has springs at the back
Critical Applications
- Busy ports with lots of traffic
- Areas with strong tides
- Permanent anchor mooring situations
4. Breast lines
Description
A breast line is a mooringline that secures the ship sideways to the dock. It is one of the key mooring lines along the dock. It stops the ship from swaying from side to side when moored.
Why It’s Better?
The breast line holds your ship so the bow cannot be pushed away from the dock. It gives you maximum safety when you are unloading cargo. This is why you need the best mooring ropes for ships.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Prevents sideways movement
- Keeps the ship close to the dock
- Uses bollards in the middle of the ship
Critical Applications
- Tight harbor berths
- Fueling operations
- When passengers are getting on or off
B. Mooring Lines By Material (High-Performance Synthetic Fibers)

Now, we will look at high-performance mooring lines for ships made from modern synthetic materials. These quality marine ropes offer amazing benefits.
1. UHMWPE (or HMPE/Dyneema®) Mooring Line
Description
A UHMWPE mooring line is a woven rope made from UHMWPE fibers, which are also known by brand names like Dyneema rope. This dynema rope is very strong and also very light. Compared to options like steel wire ropes, you will find it is a much better choice. We at Duracordix specialize in this kind of high-performance rope.
Why It’s Better?
So, why is a UHMWPE vessel mooring line better? It is 7 to 10 times stronger than a steel wire rope of the same weight. It is also 85% lighter, which makes it much easier for your crew to handle. It’s no wonder many look for dyneema rope for sale.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Has a specific gravity of 0.97
- Features a very low 3-4% elongation
- Floats on water, a key dyneema rope standard
- Also known as generic dyneema or dyneema HMPE
Critical Applications
- Heavy-duty mooring lines for ships
- Offshore mooring platforms
- Towing and salvage operations
- Mooring system offshore
- Nylon Mooring Line
2. Nylon Mooring Line
Description
These are made from nylon, which makes the nylon mooring lines very strong, stretchy, and durable. Also, nylon’s stretchy nature absorbs shock. This helps your ship handle bouncing waves and wind with ease. Many consider it the best type of rope for mooring.
Why It’s Better?
Why would you want this mooring line? Its great stretch reduces the shock on your mooring point, protecting both the vessel and the dock. These nylon lines are very reliable.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Has up to 25% elongation
- Absorbs shock loads very well
- Loses about 10-15% of its strength when wet
Critical Applications
- General purpose mooring of a ship
- Areas with rough seas
- Shock absorption needs
- Docking lines for boats
3. Polyester Mooring Line
Description
Polyester mooring ropes are made from a strong yarn that resists rubbing. It can also handle sudden shocks. And it will not lose its strength in water, unlike some nylon mooring rope options. It is a great material for your boat ropes.
Why It’s Better?
Polyester mooring lines give you great strength. They do not stretch as much as nylon ropes, which can make a vessel hard to control. These lines also give you better protection from the sun’s rays, making them one of the best mooring lines for ships.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Has a specific gravity of 1.38
- Features a low elongation of 12-18%
- Resists moisture and UV rays
Critical Applications
- Permanent anchor mooring
- Harbor and docking systems
- Offshore mooring platforms
- Best mooring lines for ships
4. Kevlar (Aramid) Rope
Description
A Kevlar rope is made from high-performance fibers. It is light and very strong. You will also find it is resistant to cuts and heat. This makes it a great choice for your ship ropes.
Why It’s Better?
In tough mooring situations, Kevlar ropes help a lot. Their 500°C melting point means they can handle extreme heat. This makes them perfect for demanding mooring systems.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Has a specific gravity of 1.44
- Features very low 4% elongation
- Has amazing heat resistance
Critical Applications
- Tanker and LNG moorings
- Fire rescue lines
- Military and tactical uses
- Navy mooring lines
C. Mooring Lines By Material (Conventional Synthetic & Metallic)

Before, we looked at high-tech fibers. Now, let’s talk about more traditional materials used for your ship mooring lines.
1. Polypropylene Mooring Line
Description
This rope for boats is made from 100% polypropylene fibers. Because it is so light, it is very easy for you to handle. Another great benefit is that it floats on water, creating a floating mooring line.
Why It’s Better?
It is very popular because of its low price and cheap replacement cost. It also helps you avoid getting tangled with things under the water.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Has a specific gravity of 0.91
- Floats on water
- Has good chemical resistance
Critical Applications
- Securing small vessels
- Buoy mooring line
- Rescue operations
2. Polyethylene Mooring Rope
Description
This rope for mooring is made from polyethylene fibers. It is very resistant to rubbing and has good UV stability. This makes it a great budget-friendly choice for marine use.
Why It’s Better?
Because it absorbs little water, it stays light and easy for you to handle. This makes it a great general-purpose marine rope.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Low water absorption
- Good UV stability
- Affordable price point
Critical Applications
- Fishing and netting
- General-purpose mooring
- Buoy lines
3. Wire Mooring Line
Description
Wire ropes are made from steel strands wrapped around each other. They are very strong when pulled, do not stretch much, and are good for a multi point mooring system. A tug mooring wire is a common example.
Why It’s Better?
They have great strength and durability. They are a must-have for very large ships. Their integrity is unmatched for heavy-duty jobs.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Very low elongation of less than 2%
- High tensile strength
- Needs regular lubrication to prevent rust
Critical Applications
- Large marine vessels
- Offshore oil platforms
- Heavy and ultra-stable anchoring systems
4. Chain
Description
A chain is the most basic mooring line you can find. It is also the heaviest of all the materials. It is best for when you need a permanent anchor mooring in shallow water.
Why It’s Better?
The chain’s strong catenary effect spreads the weight evenly. This greatly improves the anchor’s performance. Because of this, your vessel can stay in a stable position without much movement.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Strong vertical pull
- Heavy catenary effect to reduce anchor drag
- Can be used in complex anchoring systems
Critical Applications
- Permanent anchor mooring
- Shallow water moorings
- Long-term vessel storage
D. Mooring Lines By Rope Construction

How a rope is made affects how it handles and performs. Let’s look at common constructions for your ship mooring rope.
1. Three-Strand Twisted Mooring Lines
Description
These ropes are twisted into a simple spiral shape. This makes them very easy for you to splice and repair. Because of this, they are often used as backup mooring lines for boats. This is a classic three strand line.
Why It’s Better?
This type of rope construction is very cheap but offers you good stretch. It is a favorite choice for many general mooring tasks. These 3 strand dock lines are very common.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Spiral construction
- Simple to splice
- Good elasticity
- Also known as 3-strand dock lines
Critical Applications
- Mooring of boats that are small
- Temporary docking
- Utility lines
- Mooring lines for boat
2. Eight-Strand Plaited Mooring Line
Description
This rope has eight strands braided together. This gives you excellent anti-twisting features. They are much less likely to get tangled when you use them. This is a great choice for mooring ropes for large ships.
Why It’s Better?
Its construction is perfect for situations where you need high anti-twist performance. This improves the safety and efficiency of mooring in heavy-duty situations, such as a Baltic moor.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Eight braided strands
- Good anti-twist characteristics
- Resistant to tangling
Critical Applications
- Commercial shipping
- Offshore platforms
- Heavy-duty mooring situations
- Mooring ropes for large ships
3. Twelve-Strand Braided Mooring Lines
Description
These ropes have 12 strands braided in a circle. This gives them very high pulling strength. This single braid construction resists twisting. This makes it a superior vessel mooring line.
Why It’s Better?
This design gives you one of the highest tensile strengths you can find. It is best suited for your heavy-duty mooring tasks. For large vessels, these are top-tier mooring lines for ships.
What Are Its Key Features?
- 12 braided strands
- Single braid construction
- High tensile strength
Critical Applications
- Mooring of boats that are large
- Dynamic positioning systems
- Heavy-duty operations
- Can be found as used mooring lines for ships
4. Double-Braided Mooring Lines
Description
This construction has two braided layers to meet your needs. The inner core is strong. The outer cover gives you great abrasion resistance. This is the definition for mooring line. For example, a 2 double braided nylon rope is a popular choice.
Why It’s Better?
This setup ensures the core’s pulling strength is protected. That is why they are great for long-term; high-durability uses. A double braid dock line is a prime example of this technology.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Inner braided core
- Outer protective cover
- Excellent wear resistance
- Includes options like a 1 2 double braid dock line
Critical Applications
- Long-term dock mooring
- Massive ships
- Uses requiring high durability
- Personalized dock lines
5. Single-braid Ropes
Description
Single-braid ropes do not have a separate core. The strands are braided to form a single tube shape. This construction is basic, flexible, and easy for you to check. These make great boat docking ropes.
Why It’s Better?
The stiffness and smooth surface of single-braid ropes reduce rubbing and wear. It is also lighter and lasts longer than a twisted rope.
What Are Its Key Features?
- No inner core
- Tubular braided construction
- Smooth and flexible
Critical Applications
- Ropes for boats like yachts
- Mooring of boats that are light
- Utility ropes
- Dock ropes for boats
6. Square Plait / Square Braid
Description
This rope is braided with 8 or 12 strands. It is also called a square braid. It is commonly used for mooring and anchor ropes. These mooring lines ship well and are very reliable.
Why It’s Better?
It is proven to stay flexible for mooring use. It can handle heavy breaking loads for a long time. You will find it is a very dependable choice.
What Are Its Key Features?
- 8 or 12 strands
- Stays very flexible
- Handles heavy loads
Critical Applications
- Tow ropes for commercial shipping
- Anchor ropes
- Fender lines
- Marine ropes and lines
E. Specialized Mooring Lines

Some situations need special lines. Below are a few important mooring line types you should know for your mooring system.
1. Nylon Mooring Tail
Description
A mooring pendant is an extension of a mooring line. It is made of synthetic materials, in this case, nylon. It is used to cushion and protect the main rope. A double mooring pendant offers extra security.
Why It’s Better?
The high stretch reduces the peak load pressure on the mooring line. This helps to relieve shock from the line. It’s a key part of what is a mooring.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Made from 100% nylon
- Available in 8 or 12-strand designs
- Features 30% elongation
- A line snubber can offer similar benefits
Critical Applications
- Vessel mooring systems
- Offshore platforms
- Floating structures
- Use with a mooring harness
2. Polyester & Polypropylene Mooring Tail
Description
This is made by combining polyester and polypropylene fibers. The polyester gives it high strength and resistance to rubbing. The polypropylene helps it float to prevent sinking and ensures the line stays above water.
Why It’s Better?
This mix gives you a better price than pure nylon tails. It also helps reduce the chance of snagging on things under the water.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Specific gravity of about 0.92
- Melting point of 250-265°C
- Good buoyancy
Critical Applications
- Dock and port systems
- Floating storage vessels
- General mooring use
3. Mooring lines for recovery
Description
These are special rescue ropes for when a vessel gets stuck or flips over. These mooring lines in recovery are very important tools. Knowing what are mooring lines in recovery can be a lifesaver.
Why It’s Better?
They are designed for situations with high tension and sudden forces. The mooring lines definition in recovery emphasizes this strength.
What Are Its Key Features?
- Withstands high tension
- Handles heavy loads
- Resists dynamic forces
Critical Applications
- Vessel grounding incidents
- Ship capsizing events
- Retrieving drifting equipment
Key Material Properties For Mooring Lines For Ships!

Knowing the material properties is very important. This will help you choose the right mooring rope for any job.
HMPE 0.97 Gravity
An HMPE rope has a specific gravity of 0.97. It floats easily because it is less dense than water. This makes it easy for you to see and grab. It also avoids getting caught on things under the water. This makes it the ideal rope for mooring lines. The Dynamica sk78 is a great example.
Nylon 25% Elongation
Nylon is known for its high stretch and strength. It can stretch up to 25%. This ability to stretch helps the nylon mooring line absorb sudden large loads. This can save your vessel and mooring hardware from damage.
Polyester Excellent UV
Polyester has very good resistance to sunlight and bad weather. This helps it last in harsh marine conditions. This makes it ideal for long-term mooring in sunny places. This is the best of all sailboat mooring systems.
Polypropylene Floats
Polypropylene is a great mooring rope for floating aids and light-duty jobs. This is because of its good strength-to-weight ratio. Its specific gravity of 0.91 makes it easy to see floating on the water.
Steel High Durability
Steel wire ropes are some of the most durable ropes for heavy-duty jobs. They are used for large commercial ships. Their pulling strength is very high with little stretching. This answers the question of what is mooring lines.
Kevlar 500°C Melting
Kevlar rope has one of the highest temperature resistances. Its melting point is around 500°C. This makes it perfect for extreme situations. It is the best for mooring tankers and for fire rescue.
| Property | HMPE | Nylon | Polyester | Polypropylene | Steel Wire | Kevlar (Aramid) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.97 | 1.14 | 1.38 | 0.91 | 7.85 | 1.44 |
| Buoyancy | Floats | Sinks | Sinks | Floats | Sinks | Sinks |
| Elongation @ Break | 3-4% | 20-25% | 12-18% | 10-15% | <2% | 3-4% |
| Melting Point (°C) | ~145°C | ~220°C | ~260°C | ~165°C | ~1400°C | ~500°C |
| Wet Strength Loss | 0% | 10-15% | 0% | 0% | 0% (Corrodes) | ~1% |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent | Poor | Immune | Good |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good | Very Good | Poor | Good (Contact) | Excellent |
Comparison of Mooring Line Material Properties!
What Determines The Strength Of Mooring Lines For Ships?
Many factors determine a rope’s strength. You need to consider these to have a safe and reliable mooring of a ship.
1140 KN MBL
A 40-millimeter rope can have a Minimum Breaking Load (MBL) of 1140 kilonewtons. That is a very high load to carry. It makes it very safe for your crew to work with. The MBL also acts as insurance for the crew and infrastructure.
3-4% Elongation
Low stretch gives you excellent control. The line has very little stretch under load. For instance, dyneema lines only stretch 3-4%. This makes it perfect for spring line breast line docking.
Excellent Abrasion
The best mooring lines for boats need excellent abrasion resistance. In corrosive environments, this is key. Materials like polyester and UHMWPE offer you superior performance against wear and tear. A braided marine rope design helps a lot.
UV Resistance
Ship ropes must survive the sun. Polyester and UHMWPE lines are great at resisting UV rays. This means your mooring lines for ships will last longer, even in sunny climates.
Chemical Immunity
In ports, ropes can be exposed to chemicals. Materials that resist acids, alkalis, and oils are best. Polypropylene and UHMWPE offer you great chemical immunity, protecting your investment.
How To Select The Right Mooring Lines For Your Vessel?
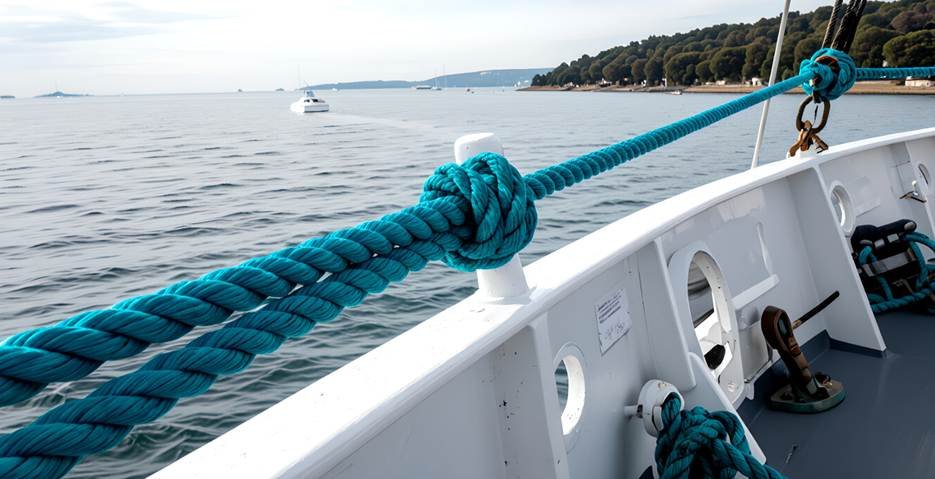

Choosing the right mooring lines for ships is about more than just picking a strong rope. You must consider several factors.
Vessel Displacement
The weight of your ship is the first thing to think about. Heavier vessels need stronger ropes. Your choice of material and diameter will depend on your ship’s displacement.
Breaking Strength
You should choose a mooring rope with a high breaking load. This allows it to hold securely in different weather. A rope’s breaking load is a key safety factor. It should be much higher than the expected load.
MEG4 Standards
Proper mooring lines for ships must meet safety rules like MEG4 standards from OCIMF. Many HMPE mooring rope products pass these tests. At Duracordix, our ropes are designed to meet these standards, giving you peace of mind.
1.5x Length
The length of a mooring rope should be 1.5 to 2 times the length of your vessel. A good rule is to multiply your boat’s length in meters by 1.5. This usually gives you enough length for tide changes.
Safety Factor
A safety factor is usually added when you decide on a rope size. Tow ropes often have a 1:2 safety factor. Lifting ropes have a 1:5 safety factor. This means the rope’s strength should be 2 to 5 times the load.
Tips For Maintaining Your Mooring Lines For Ships!
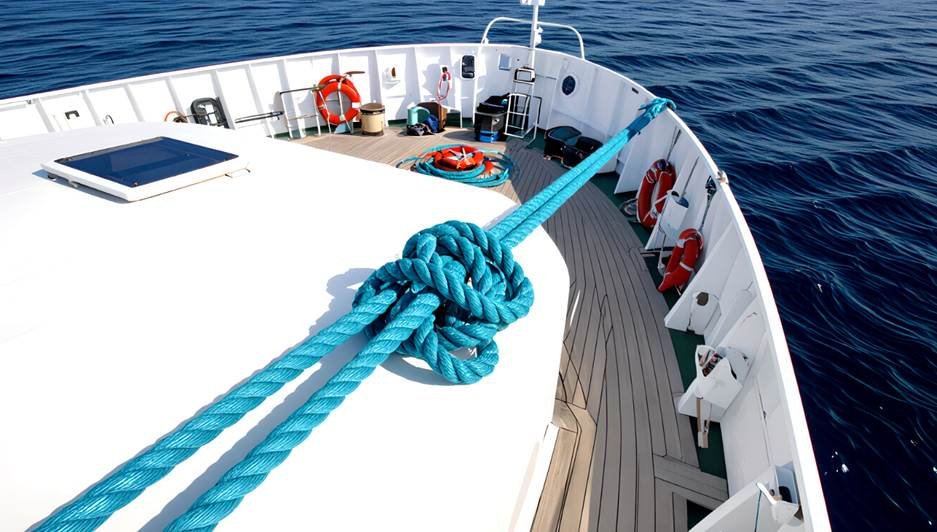

The life of your lines will be much longer if you take proper care of them. To keep your mooring equipment in good shape, follow these tips.
Regular Inspections
You should check your rope for signs of wear, rubbing, and damage. If you find wear, you might be able to cut it out. A good inspection of mooring ropes helps ensure safety.
Chafe Guards
Add mooring line chafe protection to the rope. This is very important at the eye splices. It improves resistance to rubbing and decay. This will extend the service life of your mooring lines for ships.
Proper Coiling
Store your rope neatly coiled. You can put it in a rope bag to avoid twisting or knotting. Kinks and knots can weaken the rope over time. A hawser hole is not a good storage alternative.
Freshwater Rinsing
Your rope does not need to be dirty. Rinsing it removes salt and sand. This prevents these things from getting embedded in the fibers and reducing the rope’s strength.
Dry Storage
You should store your mooring ropes in a dry, room-temperature place. Keep them away from heat, moisture, and sunlight. Proper storage is key for rope safety and a longer lifespan.
Immediate Repairs
Check your equipment for small damages. Make repairs to the rope, but check the guidelines first. Do not use broken ropes for important jobs. This helps ensure you don’t moor a boat with a broken rope.
FAQs!
These answers will help you understand the mooring definition and its details.
How Does MEG4 Define A 15:1 Bend Ratio?
Mooring ropes should not bend tighter than a 15-to-1 D/d curve. The bend’s diameter must be 15 times the rope’s diameter. This ratio protects the fibers and gear from shock.
What Is The Correct Safety Factor For Mooring Lines?
This changes depending on the situation. For mooring, a factor between 1.5 to 2 is often suggested. The rope must be 1.5 to 2 times stronger than the expected load to hold well. This is good mooring practice.
How Do You Calculate Proper Mooring Line Length?
A mooring rope is usually 1.5 to 2 times the length of the vessel. For example, a 30-meter vessel should have a 45 to 60-meter mooring rope. This helps with changes in tide and dock height.
Why Does Nylon Lose 15% Strength When Wet?
When mooring, water absorption can lower a rope’s strength. Nylon ropes absorb a lot of water. This not only ages the material but also reduces its strength by about 10-15% over its service life.
What Defines A Mooring Line Snap-Back Zone?
A mooring line snapback zone is a very dangerous area. It is where a mooring rope might whip back if it breaks. Special safety training is needed to reduce this risk. This is part of the definition of mooring lines.
Conclusion
You have now learned about the different types of ropes. These ropes are ideal for your mooring lines for ships. They provide safety for your vessel. You can find the best options at Duracordix. Please visit us to see our high-standard ropes. Our team will help you choose the perfect ropes for your needs.
About The Author

Moses Xu
Hi, I’m Moses Xu, VP and Marketing Director at Duracordix. With 10+ years in high-performance synthetic ropes and netting, I specialize in export trade and marketing. Whether it’s HMPE, Kevlar, or nylon ropes, I’m happy to share insights and connect!